Figure 10.
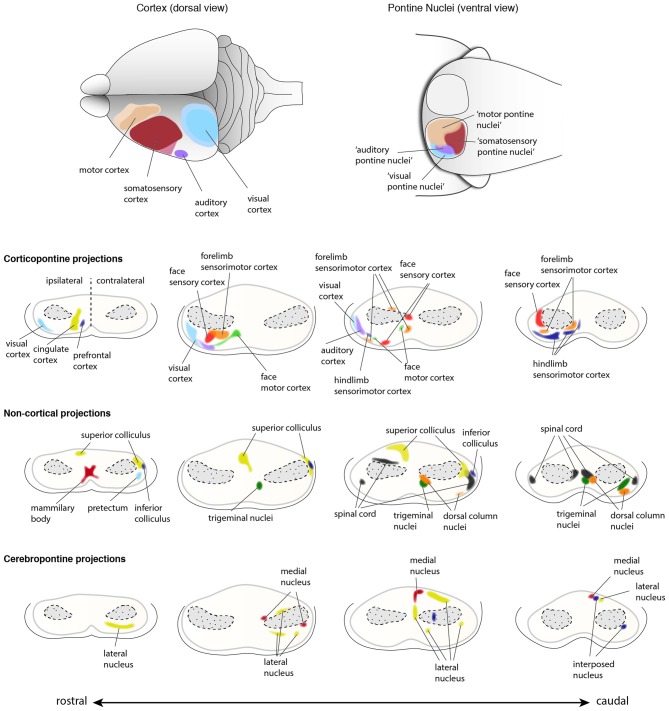
Input innervations of the PN. PN receive mainly projections from the cortex but also from subcortical regions. Using dye tracings, innervation patterns from various cortical and subcortical areas were identified. Cortical projections mainly innervate the ipsilateral PN, while subcortical projections innervate both ipsilateral and contralateral PN. The topography of cortical regions is roughly maintained in the PN (top panel), with auditory and visual cortex projecting to the dorso-lateral parts of the PN, motor cortex projecting to the rostral and medial areas and somatosensory cortex projecting to the caudal regions of the PN (Brodal, 1968; Leergaard et al., 1995, 2000, 2004, 2006; Leergaard, 2003; Odeh et al., 2005; Leergaard and Bjaalie, 2007). However, projections from distinct cortical areas may also partially overlap in the PN. Subcortical structures including superior and inferior colliculus, spinal cord, trigeminal nuclei and pretectum, and cerebellar nuclei also project to the PN (Kosinski et al., 1986). Projections from cortex and subcortical regions representing similar information often target the same PN region. (PN: pontine nuclei. Adapted with permission from Paxinos, 2014, Elsevier).