FIGURE 2.
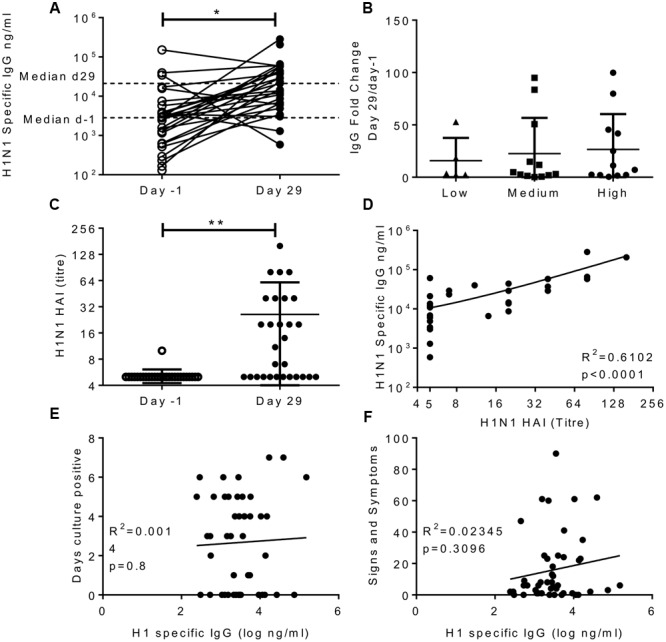
Infection with influenza increases H1 serum IgG antibody responses, but IgG does not correlate with protection. Healthy adult human volunteers were infected intranasally with different doses of H1N1 influenza (low dose: 3.5 × 104 TCID50, Medium dose: 3.5 × 105 TCID50 and high dose: 3.5 × 106 TCID50). H1 specific IgG responses were measured by ELISA in serum on day-1 and day 29 of infection and presented as absolute values (A), fold change based on the infecting dose (B). HAI was assessed at day-1 and day 29 (C) and compared with IgG titre on day 29 (D). IgG ELISA titre was compared to days culture positive (E) and cumulative signs and symptoms (F). (A–D) Represent data from a single study n = 29 volunteers, (E,F) Represent data from two studies combined n = 47.
