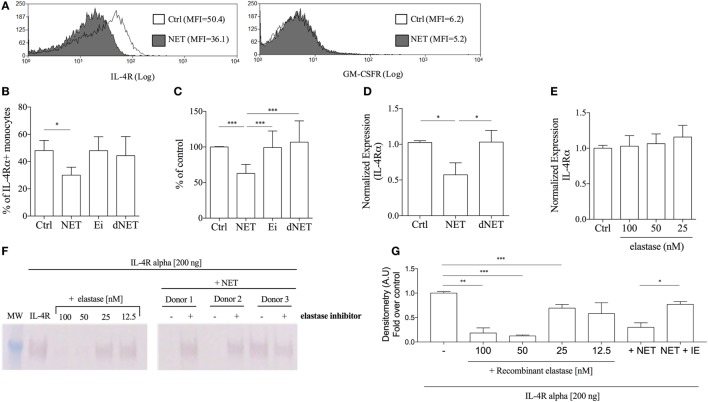
Figure 2.
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) downregulates the expression of IL-4 receptor on monocytes. (A,B) Adhered monocytes were incubated or not with NETs, which were treated or not with DNase, or elastase inhibitor for 18 h at 37°C/5%CO2. Cells were harvested and stained for the GM-CSF receptor and for the IL-4 receptor α chain after FcR blocking. (A) Histogram of one representative experiment. (B,C) Percentage of monocytes expressing the IL-4 receptor. Results of at least five independent experiments are shown as mean ± SEM. (B) Paired t-test analysis was performed and *P < 0.05 related to NETs untreated monocytes (control, ctrl). (C) ***P < 0.01. (D,E) Purified monocytes were treated or not with NETs-enriched supernatants, with digested NETs or NETs + elastase inhibitor or treated only recombinant elastase. After 4 h at 37°C/5%CO2, RNA was extracted and the cDNA synthesis was performed. Relative quantitative analysis of the target gene versus 18 s was performed using the LightCycler 480 software. Results of at least four independent experiments are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 related to the control. (F) Recombinant soluble IL-4 receptor α (200 ng) was incubated with NETs (from three different donors), pretreated (+) or not (−) with 10 µg/mL of elastase inhibitor, or with recombinant elastase in different concentrations for 30 min at 37°C. IL-4 receptor cleavage was then analyzed by western blot. (G) Densitometric analysis of the IL-4Rα chain obtained from three independent experiments were analyzed by Image J. Results were normalized by the untreated recombinant IL-4R.