FIG. 6.
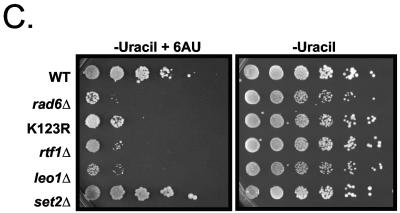
Genetic analysis of the Rad6/H2B ubiquitylation pathway reveals functional links to transcription elongation. (A) Synthetic genetic interactions of the Rad6 complex. SGA technology (53) was used to cross NatR strains harboring individual deletions of genes encoding for the Rad6 complex (rad6Δ, bre1Δ, and lge1Δ) with a transcription-targeted array of 384 Kanr deletion strains to create sets of NatR/Kanr haploid double mutants. Growth rates were assessed by automated image analysis of colony size, and lines in the diagram connect genes with synthetic genetic interactions. (B) Tetrad analysis documents the genetic interactions found between components of the Rad6 complex and other elongation-related factors identified by SGA. Genotyping of these tetrads revealed that the inviable or slowest growing colonies were the appropriate double mutants. (C) Analysis of strains carrying rad6Δ or H2B K123 tail mutations for 6-AU phenotypes. The WT Flag-H2B strain, the Flag-H2B K123R (K123R) mutant strain (YZS277), and strains with the indicated deletions made in the Flag-H2B background (see Fig. 1) were transformed with a plasmid bearing a copy of the URA3 gene (pRS316) and then plated as fivefold serial dilutions onto SD-uracil or SD-uracil containing 100 μg of 6-AU/ml. Similar results were observed by using 50 or 150 μg of 6-AU/ml, and deletions of BRE1 and LGE1 were also found to be sensitive to 6-AU (data not shown).