Figure 1.
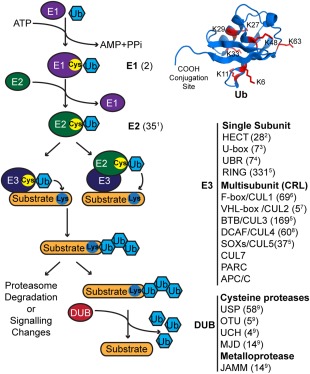
The ubiquitin proteasome system. The cartoon shows an overview of the ubiquitination process and the major components of the UPS. In the first step of Ub conjugation, E1 consumes ATP to form a high energy thioester bond between the Ub C‐terminal carboxyl group and the E1 active site cysteine thiol group. In the next step, the activated Ub is transferred to the E2 active site cysteine. In the final step, E3 mediates conjugation of the Ub C‐terminal carboxyl group to an amino group of a lysine residue in a substrate protein or another Ub molecule. In this step, the Ub is either transferred through an E3 active site cysteine (HECT E3 ligases) or directly from an E2 to the receiving lysine. DUBs catalyze the cleavage of the Ub C‐terminal carboxyl from substrate proteins or from Ub chains to reverse ubiquitination. The structure of Ub (PDB: 1UBQ) is shown (top right), indicating the location of the C‐terminal carboxyl conjugation site and the seven acceptor lysine residues, which are shown as red sticks. The number of members in each UPS family is indicated in parenthesis and was taken from the following studies: 1,7 2,8 3,9 4,10 5,11 6,12 7,13 8,14 915
