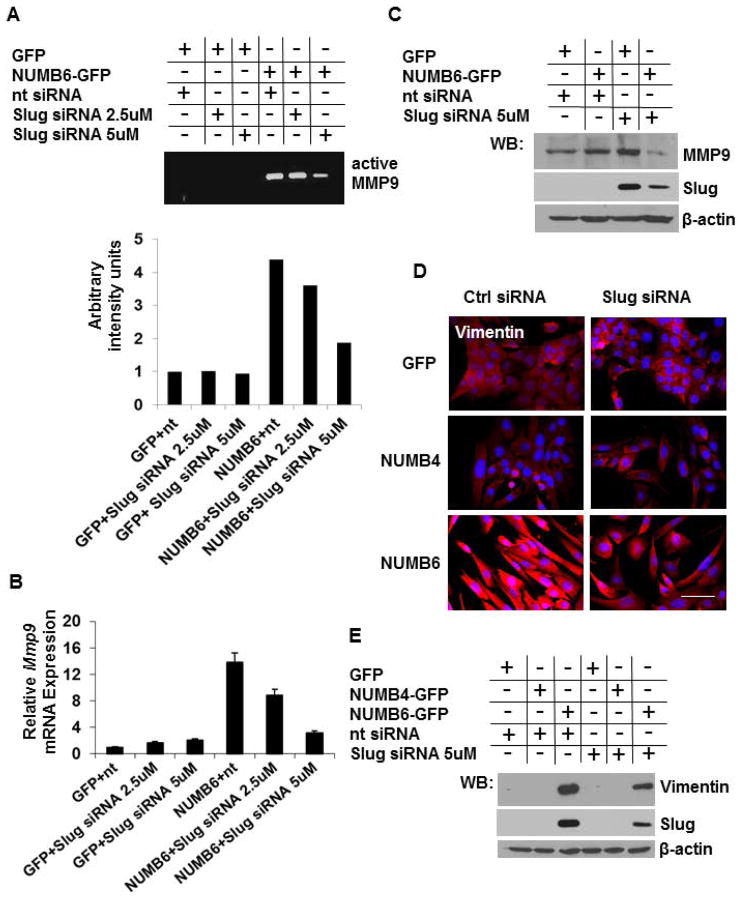
Fig. 4.
Knockdown of Slug in NUMB6-GFP DB-7 cells modulates expression of MMP9 and vimentin. (A) NUMB6-induced MMP9 activity was decreased with Slug-siRNA treatment in DB-7 cells. MMP-9 activity was assessed by zymography in conditioned media collected after 24 hr post-transfection of NUMB4-GFP, NUMB-GFP or vector control GFP DB-7 cells with Slug-siRNA or control siRNA. (B) Slug knockdown reduces Mmp9 expression in NUMB6-GFP DB-7 cells. siRNA treatment with 2.5uM or 5uM Slug siRNA reduced Mmp9 mRNA levels. The mRNA levels of Mmp9 were measured by quantitative RT-PCR analysis of total RNA extracted from NUMB4-GFP, NUMB6-GFP or control vector GFP DB-7 cells treated with Slug-siRNA or control siRNA for 48hr. The mRNA levels of Mmp9 are expressed relative to β-actin transcripts. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times. Error bars represent SEM. (C) Expression level of MMP9 protein was decreased in Slug-depleted NUMB6-GFP DB-7 cells. NUMB4-GFP, NUMB6-GFP and control vector GFP DB-7 cells were transfected with control siRNA or Slug 5uM siRNAs for 48hr. Expression levels of MMP9 and Slug were analyzed by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as loading control. (D) Decreased expression of vimentin resulted from Slug knockdown of NUMB6-GFP DB-7 cells was confirmed by immunofluorescence staining. Alexa-Fluor 594 conjugated anti-mouse IgG was used as a secondary antibody against vimentin (red). Blue is staining for nuclei. Bars=15um. (E) Western blot shows that vimentin protein was reduced in Slug-depleted NUMB6-GFP DB-7 cells. NUMB4-GFP, NUMB6-GFP and control vector GFP DB-7 cells were transfected with control siRNA or Slug 5μM siRNAs for 48hr. β-actin was used as loading control.