Figure 3.
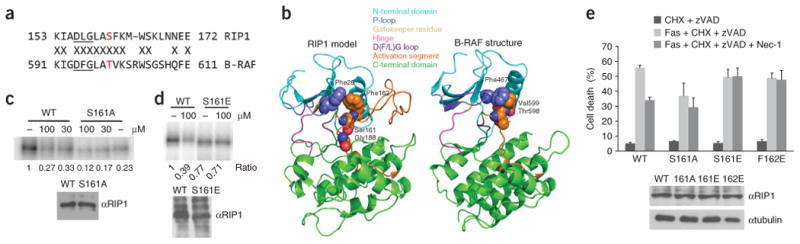
Effect of Ser161 and Phe162 mutations on necroptosis and inhibition by 1. (a) Sequence alignment of the magnesium binding and activation segments of B-RAF and RIP1. Thr598 of B-RAF and Ser161 of RIP1 are shown in red. Kinase-conserved DFG motif is underlined. (b) Homology model of RIP1. (c,d) S161A (c) and S161E (d) mutations attenuate RIP1 kinase sensitivity to 1 in vitro. Kinase assays of RIP1 mutants overexpressed in 293T cells were performed as described in Figure 1. “–” indicates DMSO. In parallel to kinase reactions, a sample of beads was subjected to western blot analysis using anti-RIP1 antibody to ensure equal protein amounts in kinase reactions. Assays were performed at least two or three times, and similar results were obtained each time. The representative images are shown. (e) Mutations of Ser161 and Phe162 attenuate inhibition of necroptosis by 1. Corresponding pcDNA-FLAG-RIP1 vectors were transiently electroporated into RIP1-deficient Jurkat cells along with pEGFP. Cells were allowed to recover for 48 h, treated with anti-FAS antibody, cycloheximide and zVAD-fmk to induce necroptosis and 30 μM 1, followed by analysis by FACS as described in the Methods. The data were obtained in a single experiment performed in triplicate and represent mean values ± s.d. Experiment was repeated multiple times, and similar results were obtained each time. Equal expression of RIP1 mutants was confirmed by western blot using anti-RIP1 and anti-tubulin antibodies.
