Figure 1.
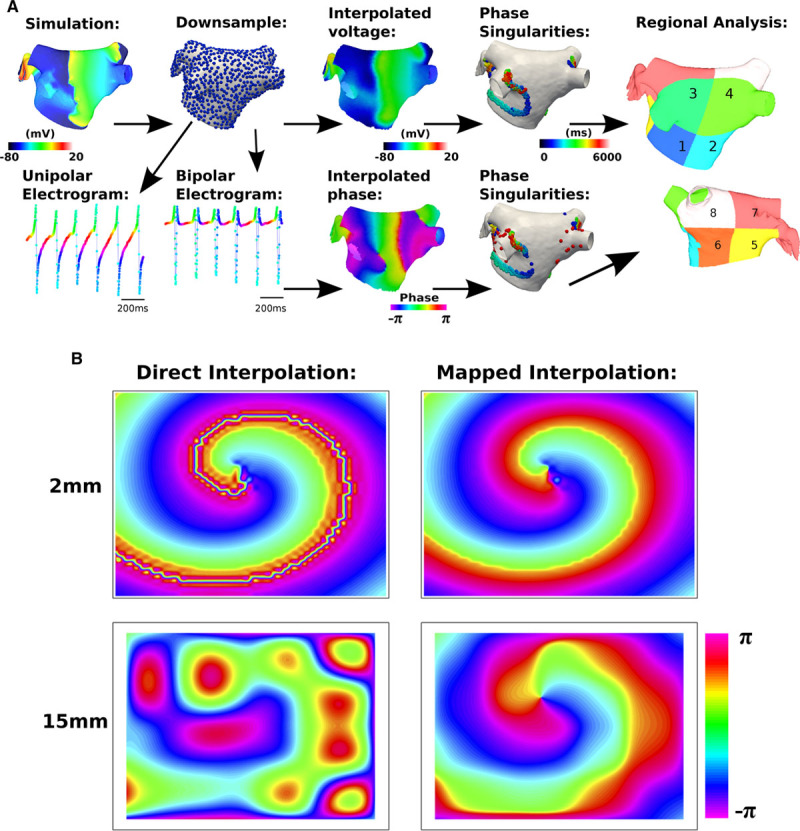
Methods schematic. A, Action potential (AP) data were computed at a mesh resolution (MR) of 0.34 mm edge length (93 927 points). Data were then downsampled: 1.62 to 17.1 mm (4813–36 points). Voltages were interpolated (to MR=1.62 mm), and phase was calculated. Unipolar electrograms were calculated at AP point distribution. Bipolar electrograms were calculated from paired unipolar electrograms with 4-mm interelectrode spacing. Phase of unipolar and bipolar electrograms was calculated and interpolated to MR=1.62 mm. Phase singularities were tracked over time (>120 ms trajectories tagged as rotors), and regional assessment was performed. B, A mapping is introduced for phase interpolation. Direct interpolation of the phase angle θ leads to issues when interpolating, in the instance that neighboring points are close to π and −π (left). Mapping to the exponential form (eiϑ), interpolating this and then converting back to a phase angle, removes the issue with phase angle discontinuities (right). The errors become larger as the grid spacing is increased (bottom). The domain size shown here is 10 cm-by-10 cm.
