FIGURE 1.
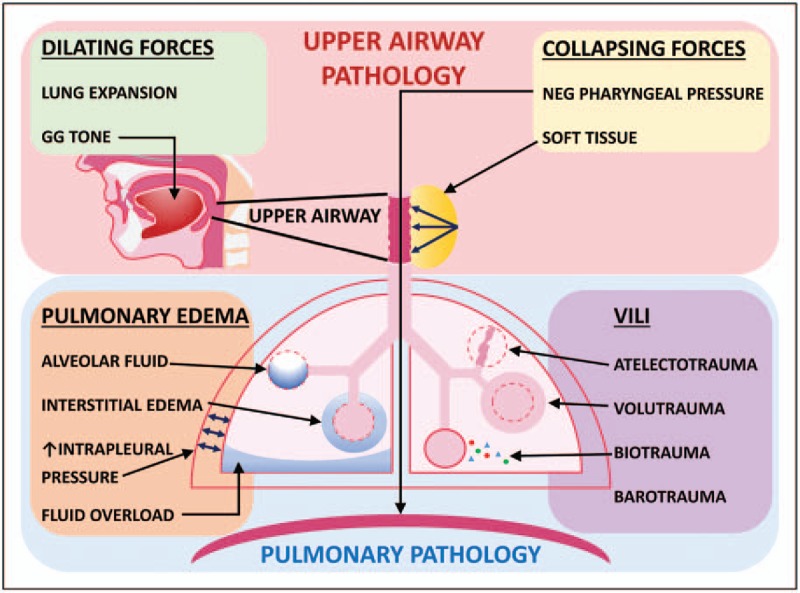
Upper airway and pulmonary disorders. Upper airway disorders are given in the pink box. Dilating forces (green box) include increased lung expansion and increased upper airway dilator muscle tone (genioglossus muscle shown). Collapsing forces (yellow box) include increased negative pharyngeal pressure generated by respiratory pump muscles (diaphragm shown), and increased soft tissue causing external mechanical load on the upper airway (yellow mass with arrows next to upper airway). Pulmonary disorders are given in the blue box. Pulmonary edema (orange box) with interstitial fluid (alveolus with surrounding fluid), alveolar fluid (blue alveolus), or both, can be caused by increased negative pulmonary pressure (blue arrows), fluid overload (blue base of lung), or multiple causes of interstitial edema. Ventilator-induced lung injury (purple box) can be due to barotrauma, atelectotrauma (deflated alveolus), biotrauma (multicolored dots), or volutrauma (distended alveolus). GG, genioglossus muscle; UA, upper airway; VILI, ventilator-induced lung injury.
