Figure 1.
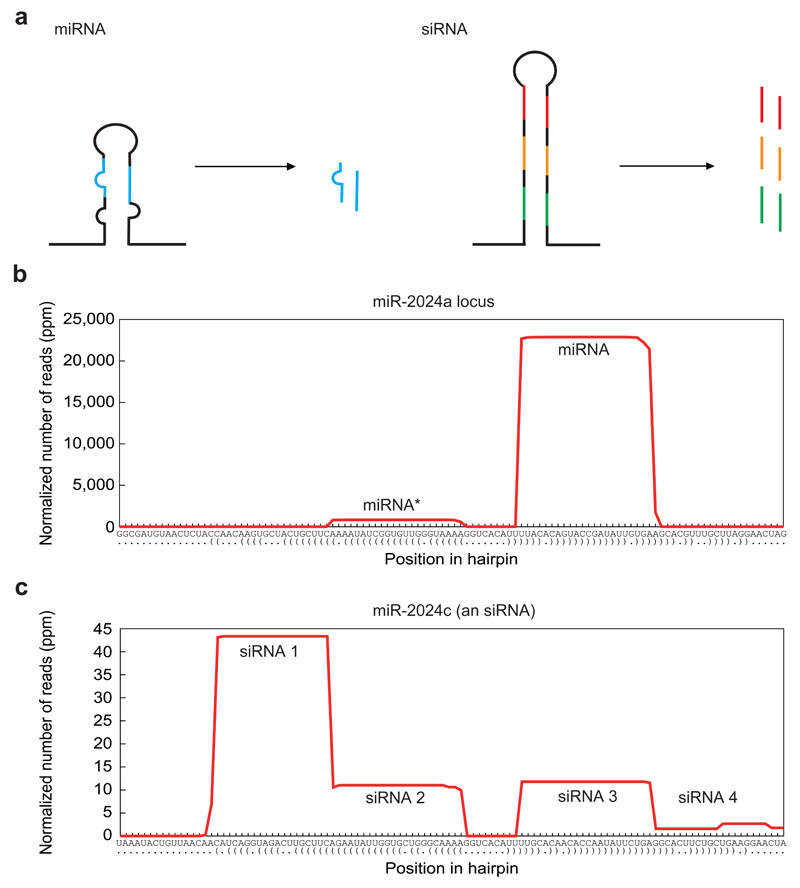
Differences between miRNAs and siRNAs. a, A scheme of miRNA and siRNA precursors and duplexes. While miRNAs are usually produced from short hairpins carrying mismatches in their stem region, siRNAs are produced from long hairpins with stems of perfect complementarity. miRNA precursors usually give rise to a single duplex whereas siRNA precursors are a source for multiple duplexes. b, Small RNA profiles along a pre-miRNA sequence, here exemplified by miR-2024a of Nematostella vectensis. Note the homogenous product with the dominant guide strand (mature miRNA) and the neglectable passenger strand (miRNA*). c, Small RNA profiles along an siRNA precursor sequence, here exemplified by miR-2024c of N. vectensis. This siRNA locus was originally annotated as miRNA, but later determined to be an siRNA due to the fact it gives rise to multiple small RNAs 45. The x-axis in b) and c) indicates the position along the hairpin sequence with paired (brackets) and unpaired nucleotides (dots). ppm = parts per million. (b and c) modified from 45, with permission.