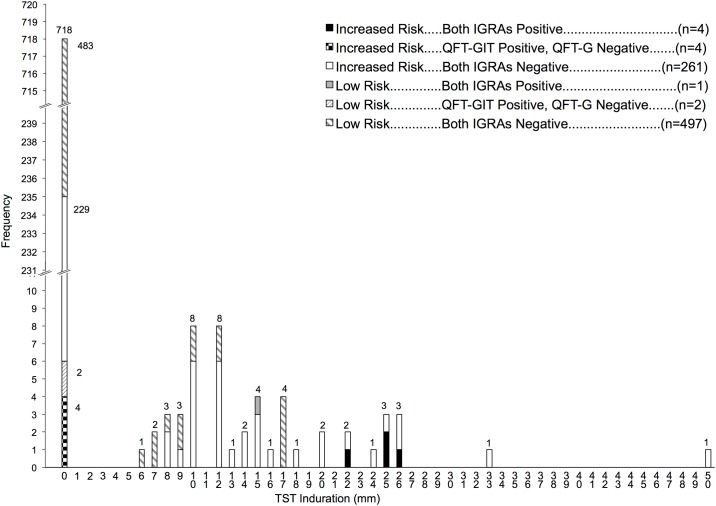
Fig 2. Comparison of QuantiFERON®-TB Gold In-Tube test, tuberculin skin test, and QuantiFERON®-TB Gold test results among 769 U.S. Navy recruits categorized by risk of M. tuberculosis infection.
The 769 Navy recruits who had TST, QFT-G, and QFT-GIT completed with determinate test results were categorized as having an “increased risk” for M. tuberculosis infection if they did not meet the “tuberculosis-suspect” criteria, but reported contact with someone with TB, birth (or residence >1 month) in a country where estimated TB prevalence in 1990 exceeded 20 cases per 100,000 population, or having resided, worked, or volunteered >1 month in a homeless shelter, prison, drug rehabilitation unit, hospital, or nursing home; or as having a “low risk” for M. tuberculosis infection if they were neither suspects nor at increased risk. IGRAs = interferon gamma release assays; QFT-GIT = QuantiFERON®-TB Gold In-Tube test; QFT-G = QuantiFERON®-TB Gold test; TST = tuberculin skin test.