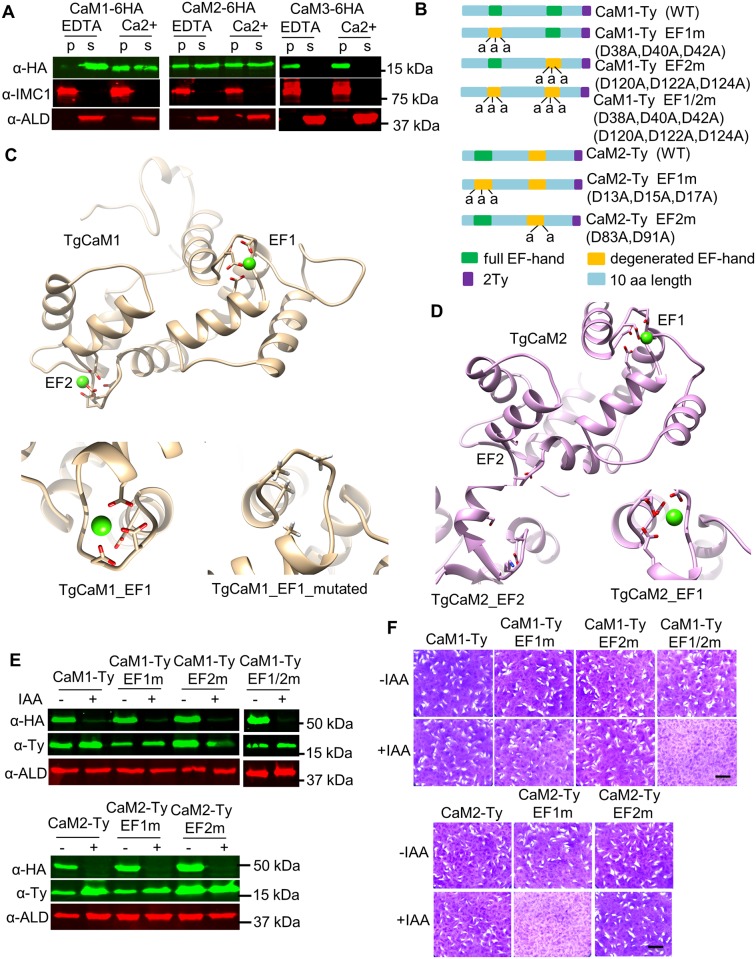
Fig 6. Assessment of the roles of EF hand domains in CaM1 and CaM2.
A. Calcium-dependent solubility as detected by cell fractionation and Western blotting. Tagged parasites were lysed in 1% Triton X-100 in the presence of either 5 mM EDTA or 5 mM CaCl2 and fractionated by centrifugation. CaM1, CaM2, or CaM3 were detected with mouse anti-HA (green), while mouse anti-IMC1 was used as a control for the pellet (p) and rabbit anti-aldolase (ALD) was used as a control for the supernatant (s). B. Diagram of wild type (WT) and CaM1 and CaM2 mutants showing the residues in conserved or degenerated EF hands (predicted by ScanProsite). Names of the proteins are shown to the right (i.e. D38A represents an Asp residue at D38 that was mutated to Ala). C and D. Structural modeling of TgCaM1 (C), TgCaM2 (D) highlighting their EF hand domains. C, Top: Structure of TgCaM1 is shown with conserved Asp residues (red) chelating a calcium iron (green ball). Bottom: enlargement of the TgCaM1 EF1 domain showing the wild type (left) and the triple EF1m mutant (right). D, Top: The structure of TgCaM2 is shown with conserved Asp residues (red) in the EF1 but not in EF2. Bottom: enlargement of TgCaM2-EF1 showing intact EF1 domain that chelate calcium (right) and the degenerate EF2 domain (left). E. Western blot detection of CaM mutants grown for 2 days ± IAA (500 μM vs 0.1% ethanol). Cell pellets were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Western blotted using mouse anti-HA to detect CaM-AID fusions, mouse anti-Ty to detect complementing alleles, and rabbit anti-aldolase (ALD) antibodies as a loading control. F. Evaluation of complementation by plaque formation. Scale bar, 0.5 cm.