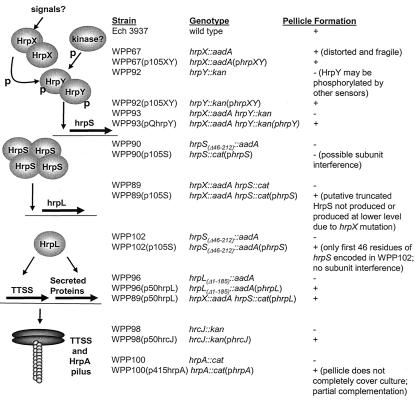
FIG. 3.
Model of TTSS regulatory cascade and table of mutant phenotypes. The TTSS regulatory cascade is shown on the left and the pellicle phenotypes of the mutants are shown on the right. The TTSS regulators HrpX and HrpY (two-component sensor kinase homolog and response regulator homolog, respectively), HrpS (a σ54-EBP homolog), and HrpL (a σ factor homolog) are all required for wild-type pellicle formation. Unlike all other TTSS mutants tested, WPP67 is able to form a pellicle, albeit a weak and distorted one. Although HrpX and HrpY are cognate sensor kinase and response regulator homologs, the phenotypes of WPP67 and WPP92 are not identical. In the diagram, the ovals and horizontal arrows symbolize proteins and genes, respectively. The vertical arrows indicate activation of genes by specific regulatory proteins. p, phosphorylation of HrpY by HrpX and possibly by other kinases. HrpX, HrpY, and HrpS homologs form multimers, which is why these proteins are shown here as multimers, although the multimerization levels for HrpX, HrpY, and HrpS are unknown. Two secretion system structural genes, hrcJ and hrpA, are also required for pellicle formation. Based on homology to other TTSSs, HrcJ is a membrane protein, and HrpA forms the TTSS pilus.