Figure 1. Stages of meiotic maturation in mouse oocytes.
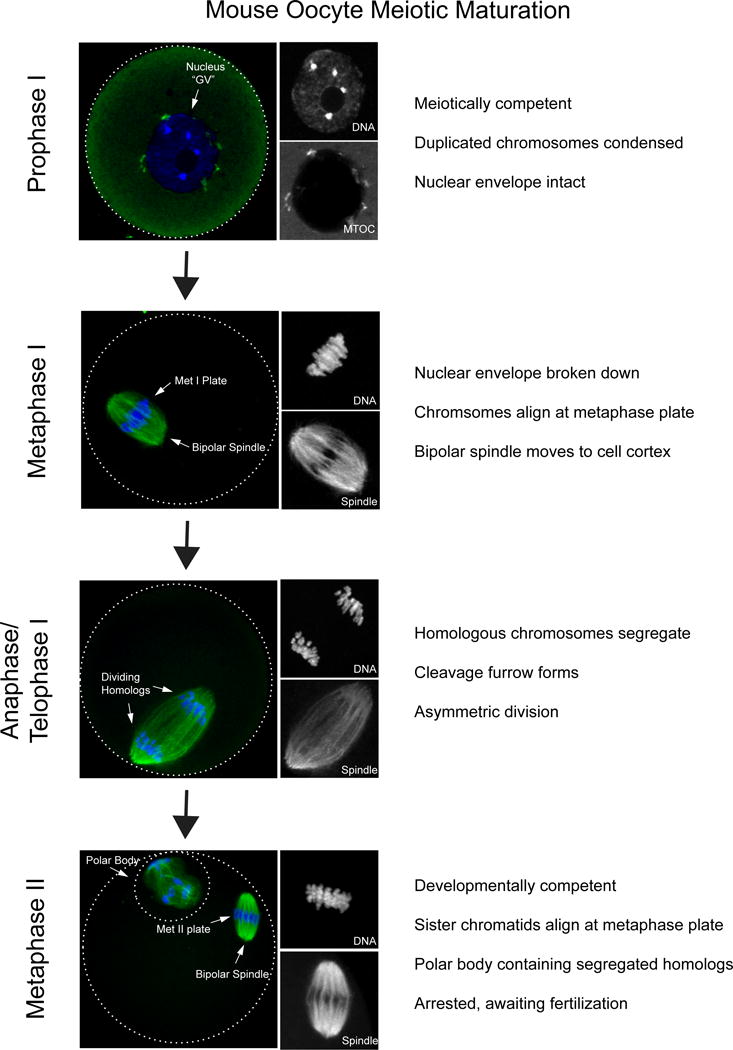
Prophase I-arrested oocytes from CF1 mice were matured in vitro to the various stages in meiosis; prophase I (0h), Metaphase I (7h), Anaphase (10h), Metaphase II (16h) prior to fixation and immunocytochemistry to detect spindle (α-tubulin; green in merge) and DNA (DAPI, blue in merge). Optical zoom images of DNA and spindle are shown on the right in grey. In prophase I the nucleus, classically referred to as the germinal vesicle (GV), remains intact. The nucleolus is visible at the center of the nucleus. Microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs; green) are attached to the nuclear membrane. Once meiosis resumes chromosomes align along the metaphase plate, organized by a bipolar spindle that moves to the cell cortex. In anaphase/telophase I homologous chromosomes are segregated. In metaphase II a polar body is visible, containing half of the chromosome compliment. Within the main body of the egg sister chromatids align along a metaphase plate and the cell arrests until fertilized by sperm.
