Fig. 1. Schematic of the UV-PAM system for surgical margin imaging.
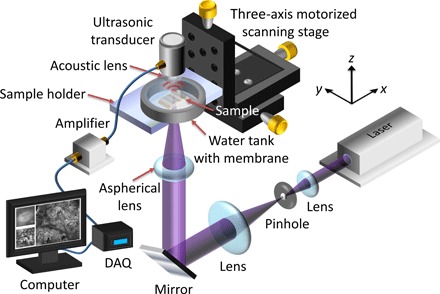
The UV laser beam is first spatially filtered and expanded by a pair of lenses and a pinhole. The beam is then focused through an aspherical lens onto the bottom of the breast tissue specimen (sample), which is placed inside a water tank on top of a sample holder. Some generated acoustic waves propagate through the tissue and reach a focused ultrasonic transducer. The received acoustic pressure is transduced into an electric signal, which is then amplified and recorded by a data acquisition (DAQ) card. During data acquisition, a maximum amplitude projection (MAP) image from the measured B-scan data is displayed on a computer screen within approximately 1 s. By raster-scanning the sample holder, a MAP image from the C-scan data is also displayed.
