Fig. 3. The regeneration process.
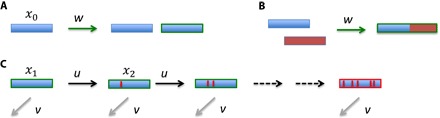
Gene duplication (A) or recombination (B) generates a starting condition for the search process, at rate w. (C) From the starting condition, we require k mutational steps, each at rate u, to reach the target sequence, which encodes a new function. At each step, there is the possibility to receive inactivating mutations, at rate v, which destroy the search. The frequency of the wild type is denoted by x0. The frequencies of the intermediate steps in the search process are denoted by xi. At steady state and assuming neutrality, we have the following frequencies: and . Let us consider a numerical example: w = 10−7, u = 10−9, v = 10−7 per cell division. Then, cells that have made as many as 10 steps toward the target have a frequency of about 5 × 10−19 and are present on a planetary scale with a total cell number of the order on 1030.
