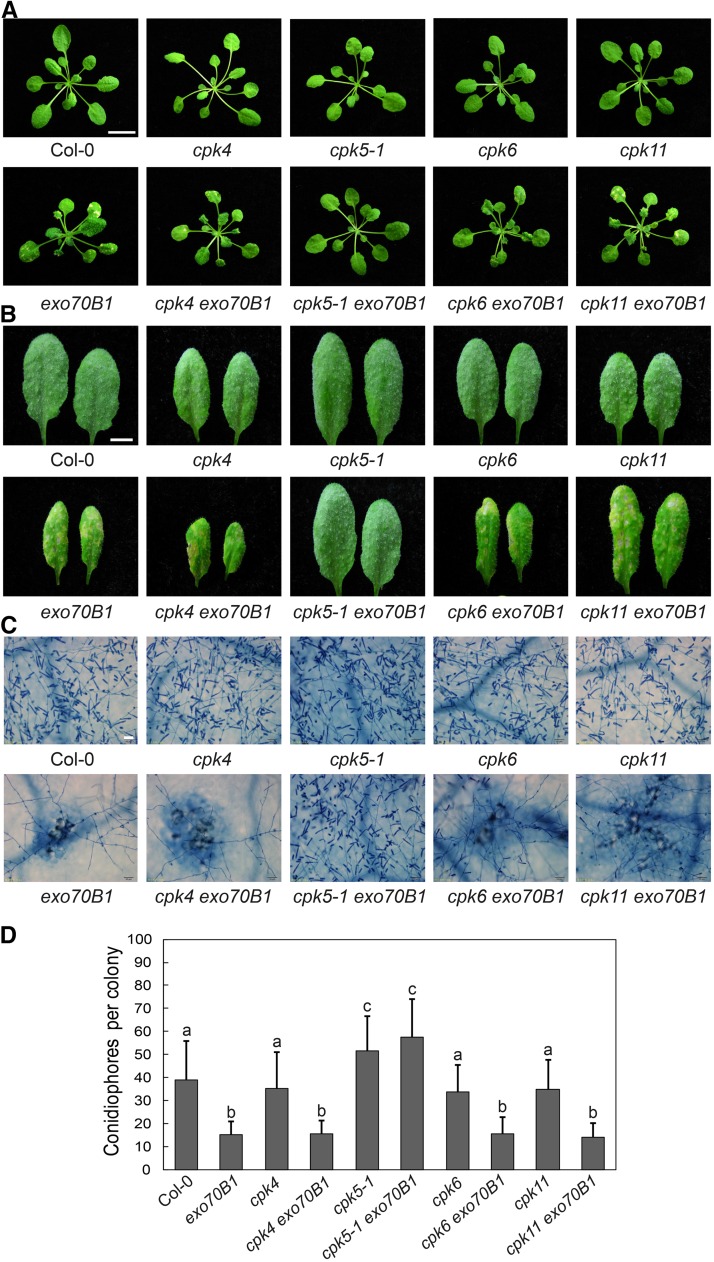
Figure 2.
Crosses with Mutants of CPK4, CPK6, and CPK11 Failed to Suppress exo70B1-3-Mediated Cell Death and Resistance to G. cichoracearum.
(A) Five-week-old plants were photographed under short-day conditions. The cpk4 exo70B1-3, cpk6 exo70B1-3, and cpk11 exo70B1-3 mutants displayed hypersensitive response-like cell death, which was similar to exo70B1-3, but no cell death was observed in the wild type or the cpk5-1 exo70B1-3 mutants. Bar = 1.2 cm.
(B) Four-week-old plants were infected with G. cichoracearum. The leaves were detached and photographed at 8 dpi. The cpk4 exo70B1-3, cpk6 exo70B1-3, and cpk11 exo70B1-3 mutants displayed exo70B1-3-like phenotypes, as they supported much less fungal growth and showed obvious mesophyll cell death compared with cpk5-1 exo70B1-3 and the wild type. Bar = 0.5 cm.
(C) The leaves were stained with trypan blue after infection with G. cichoracearum at 8 dpi. Bar = 50 μm.
(D) Quantification of fungal growth in plants at 5 dpi by counting the number of conidiophores per colony. Bars represent means and sd (n ≥ 20). Lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). The experiment was performed three times with similar results.
“exo70B1” indicates plants carrying the exo70B1-3 allele.