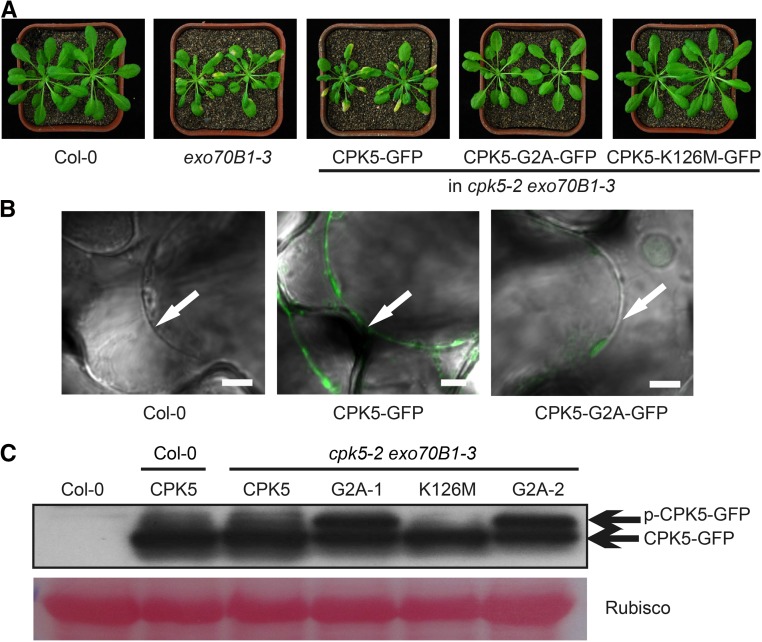
Figure 4.
Gly, the Second Residue of CPK5, Is Critical for Its Function, and the G2A Mutation Enhances CPK5 Phosphorylation.
(A) Six-week-old plants were photographed under short-day conditions. Cell death was observed in the exo70B1-3 mutant and in cpk5-2 exo70B1-3 transgenic plants carrying CPK5-GFP, but not CPK5-G2A-GFP or CPK5-K126M-GFP.
(B) Four-week-old leaves were soaked in 0.85 M NaCl for 15 min and examined by confocal microscopy. Arrows indicate plasma membrane. Bar = 5 μm.
(C) Various forms of CPK5-GFP protein were examined by immunoblot analysis. CPK5, G2A, and K126M indicate plants carrying CPK5-GFP, CPK5-G2A-GFP, or CPK5-K126M-GFP, respectively. G2A-1 and G2A-2 represent two independent transgenic plants carrying CPK5-G2A-GFP. Ponceau S staining of Rubisco is shown as a protein loading control. Bands corresponding to the phosphorylated or unphosphorylated form of CPK5-GFP are indicated by p-CPK5-GFP or CPK5-GFP, respectively.