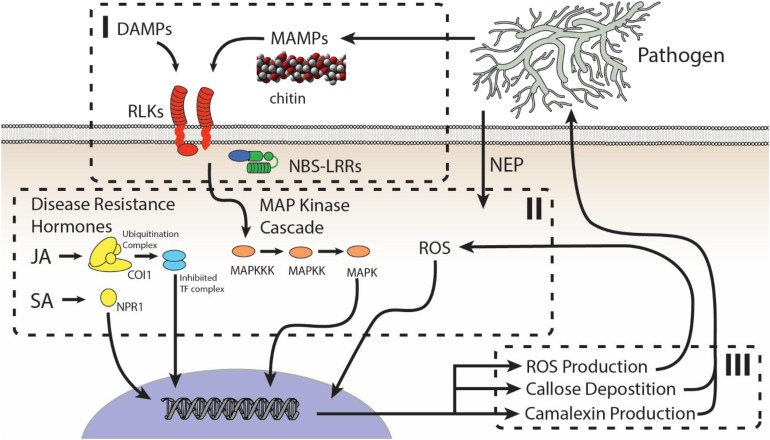
Figure 2.
General Model for the Plant Innate Immune System.
The model can be split into (I) perception, (II) signal transduction, and (III) defense response. (I) Plant perception of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and MAMPs or PAMPs are detected either apoplastically via RLKs or symplastically via cytoplasmic NBS-LRRs. (II) Signal transduction of DAMPs and MAMPs is performed by the MAP kinase cascade and a series of transcription factors, including members of the WRKY family (not depicted). (III) Signal transduction drives the production of specific defense responses, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, callose deposition, and other specialized metabolism (represented here as camalexin). Importantly, the type of defense response can be shaped by either salicylic acid (SA) to drive responses to biotrophic pathogens or JA to drive responses to necrotrophic pathogens and herbivores. In addition, ROS may play a role, both as a defense response (III) and a signal for shaping defense responses (II). NEP, necrosis and ethylene-inducing proteins.