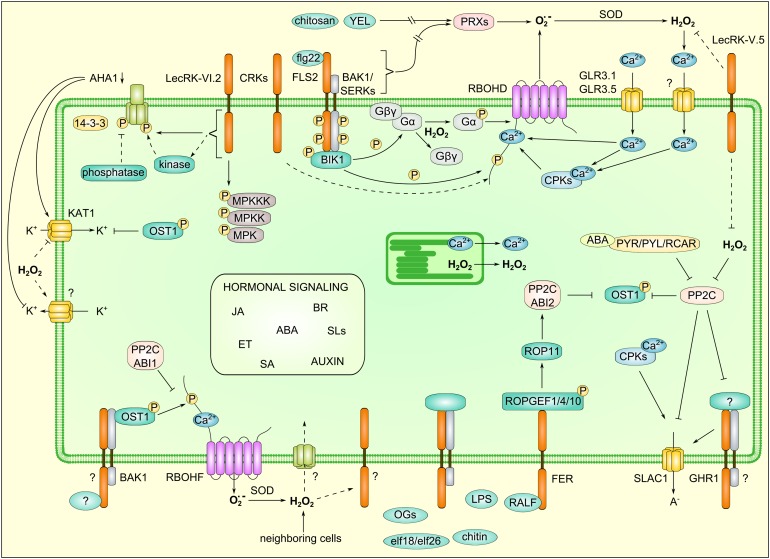
Figure 3.
Integration of RLKs and ROS Signaling in the Control of Guard Cell Closure.
Stomatal closure is controlled by a complex interplay of signaling pathways dependent on ABA and MAMP signaling that involve numerous RLK- and ROS-dependent events. The figure displays a single guard cell with signaling components that have been shown to control stomatal closure. RLKs are involved in initial MAMP perception, regulation of ROS production, and control of ion channels. Detailed descriptions of specific regulatory mechanisms are in the main text. ET, ethylene; GLR, GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR; JA, jasmonates; KAT1, POTASSIUM CHANNEL IN ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA1; PP2C, PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 2C; PYR, PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE; PYL, PYR1-LIKE; RCAR, REGULATORY COMPONENTS OF ABA RECEPTOR; SA, salicylic acid; SERK, SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE; SLs, strigolactones; SOD, superoxide dismutase; YEL, yeast elicitor.