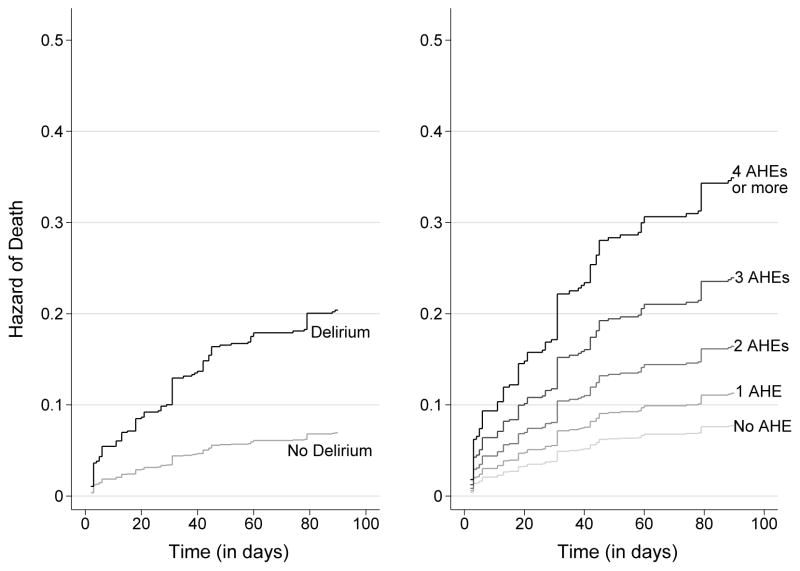
Figure 1. Cumulative Hazard of Death Associated with Delirium and the Number of Adverse Hospital Exposures.
The left panel shows data for the cumulative hazard of death associated with incident delirium in the 90 days after hospital admission. Results are adjusted for the presence of adverse hospital exposures, which include the use of physical restraints, use of a urinary catheter, occurrence of a fall, occurrence of a pressure ulcer, occurrence of sleep deprivation, occurrence of acute malnutrition, occurrence of dehydration, and occurrence of aspiration pneumonia. The right panel shows data for the cumulative hazard of death associated with the number of adverse hospital exposures, which include the use of physical restraints, use of a urinary catheter, occurrence of a fall, occurrence of a pressure ulcer, occurrence of sleep deprivation, occurrence of acute malnutrition, occurrence of dehydration, and occurrence of aspiration pneumonia. Results are adjusted for the presence of incident delirium. AHE=Adverse Hospital Exposure.