Figure 4.
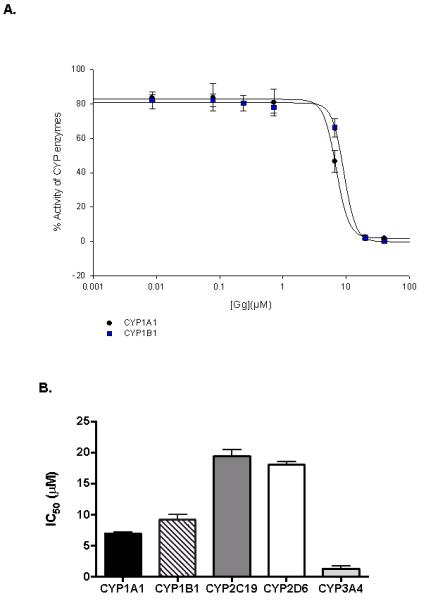
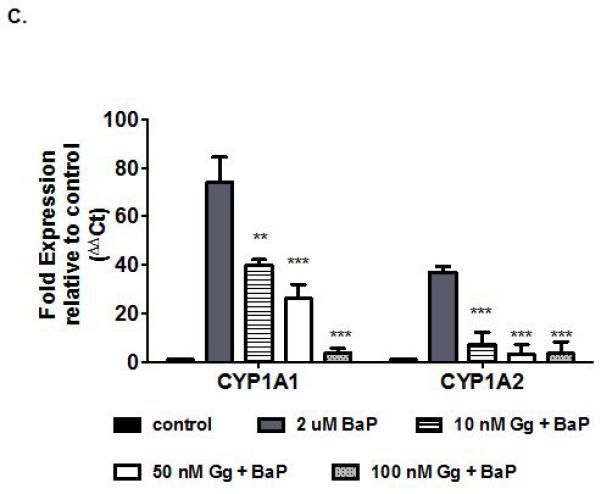
Gg inhibits CYP1 enzyme activities and suppresses B[a]P-induced CYP1A gene expression in non-invasive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. (A) Human recombinant CYP1B1-catalysed 7-ethoxyresorufin activity (0.37μM), CYPs 1A1 catalysed 7-ethoxy-3-cyanocoumarin deethylase activity (0.5μM), were determined in the presence of varying concentrations of Gg (0-20μM, as described in Materials and Methods for IC50 determinations. Control enzyme activity (mean ± SEM) for CYPs 1B1 and 1A1 were 0.34 ± 0.08, 0.86 ± 0.01 μM/min/pmol of CYP respectively. (B) Human recombinant CYP activity (as indicated by relative fluorescence) for isoforms CYP1A1, CYP1B1, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 following treatment with Gg reported as IC50 values in accordance with Materials and Methods. Results are represented as the mean of at least three independent experiments ±SEM. (C) MCF-7 cells were exposed to B[a]P alone or in combination with Gg at indicated concentrations for 24 h. Cells were harvested, RNA extracted and quantitative real-time PCR analysis performed in accordance with Materials and methods to evaluate CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 mRNA expression. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance as indicated by ** P< 0.01 or ***P < 0.001 versus treatment with B[a]P only.
