Figure 3.
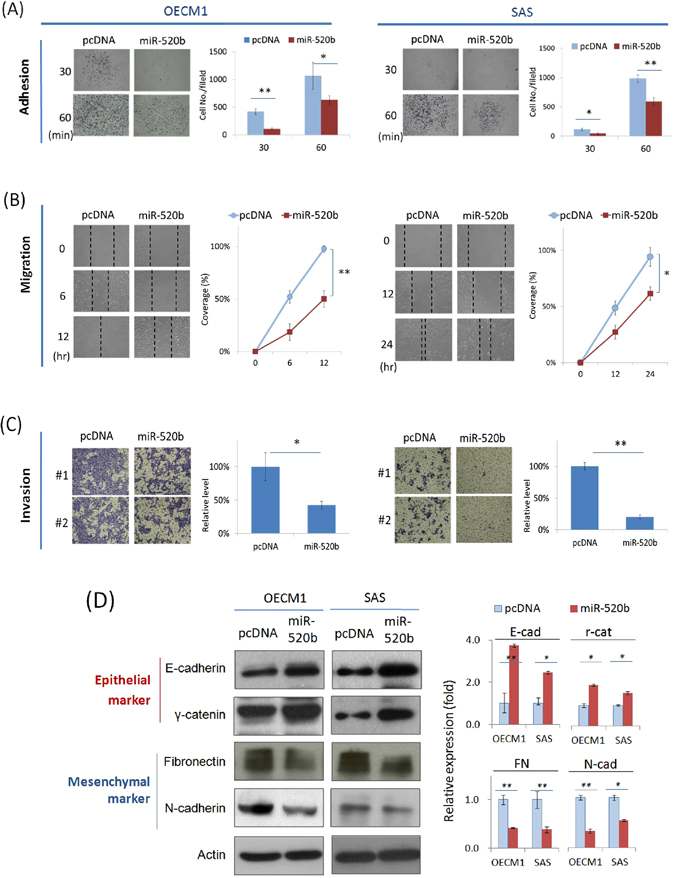
MiR-520b attenuates cell motility and invasion through suppression of EMT. After transfection of miR-520b over-expression plasmids, the HNC cells (OECM1, SAS) were subjected to adhesion, migration and invasion assays as described in the Methods section. (A) Mir-520b inhibited cell adhesion. After seeding the miR-520b- or vector- transfected cells into Matrigel coated wells for 30 or 60 mins, the attached cells were stained, photographed and quantified. (B) Mir-520b inhibited cell migration. After seeding the miR-520b- or vector- transfected cells into ibidi® culture inserts for 0–12 hrs, cells were subjected to migration analysis as described in the Methods section. Cell migration toward the gap was observed, photographed, and quantified at the indicated times. (C) Mir-520b inhibited cell invasion. After seeding the miR-520b- or vector- transfected cells into Matrigel coated membranes for 24 hrs, the cells were subjected to a Matrigel invasion assay as described in the Methods section. The cells that invaded through the Matrigel-coated membranes to the reverse side were stained, photographed, and quantified. (D) MiR-520b modulated the expressions of epithelial and mesenchymal marker proteins. After transfection of miR-520b- or the vector plasmids for 24 hrs, cellular proteins were extracted and subjected to western blot analysis for the EMT proteins (E-cadherin, r-catenin, fibronectin, N-cadherin). Actin levels were used as an internal control. The relative density of each sample was determined after normalization to the actin level. All the experiments were performed three times independently and that typical results were shown. The error bars shown in the relevant figures indicated the standard deviation of the quantification results in all experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, t-test).
