Figure 1.
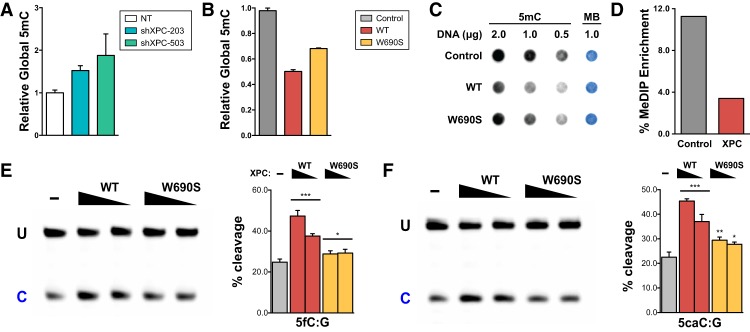
Global DNA methylation is inversely correlated with XPC expression independent of DNA repair activity. Relative global DNA methylation was assayed by 5mC-specific ELISA using genomic DNA from XPC knockdown H9 human ESCs (A) and HDFs overexpressing wild-type (WT) or DNA repair-deficient (W690S) human XPC (B). Relative global DNA methylation in HDFs was also assayed by 5mC dot blot (C) and MeDIP enrichment (D). Methylene blue (MB) staining was used to control for total DNA transferred to the membrane. (E,F) TDG cleavage activity of a 5′-labeled 37mer double-stranded oligonucleotide DNA (0.2 µM) in the presence or absence of decreasing amounts of wild-type or W690S mutant XPC (0.2–0.4 µM). The 37mer dsDNA contains either a 5fC:G (E) or 5caC:G (F) base pair as substrate for TDG. Uncleaved intact 37mer (U) and its cleaved product (C) were separated on a denaturing PAGE gel. Representative gels are shown. The intensity of the cleaved product indicates the efficiency of base excision by TDG and is calculated in the graphs as the percentage of total labeled substrate [=C/(U + C)]. Error bars represent the standard deviation. n = 3. (***) P < 0.001; (**) P < 0.01; (*) P < 0.05, calculated by two-way ANOVA.