Figure 8. Whole‐cell voltage recording and receptive field (RF) mapping of cortical cells identified post hoc in the vibrissal area of somatosensory cortex (vS1).
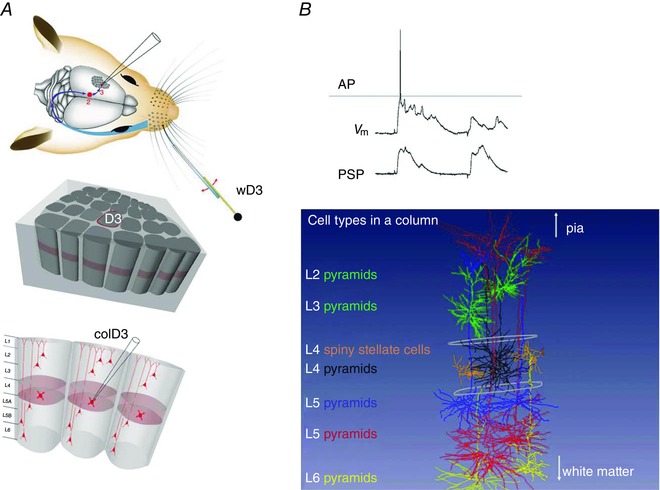
A, anatomy of the whisker system at different resolutions. Top panel, topology of the afferent lemniscal pathway from facial whisker pad to vS1 cortex (blue arrows). Deflection of whisker D3 by a piezo actuator. Middle and bottom panels, column D3, with upper circumference highlighted in red, is driven by whisker wD3 and is designated as the principal whisker column (PW column). The vertical division of columnar layers into granular (light red), supragranular and infragranular layers, respectively, is shown in the lower panel. Schematic drawing of the whisker system in the top panel is modified from Knott et al. (2002). B, upper panel, voltage recording of whisker‐evoked sub‐ and suprathreshold responses from a spiny stellate cell located in L4 of the PW column. Upper trace, single postsynaptic potential (PSP) response eliciting an AP. Lower trace, averaged PSP responses. From Brecht & Sakmann (2002 b), with permission. Lower panel, examples of recorded and post hoc three‐dimensionally (3D) reconstructed cells that are registered into a column in silico. Column length is ∼2 mm (in rats). This value is the distance between the pia and white matter. The column width is given by the outlines of barrels (diameter of ∼350 μm) in the granular layer (indicated schematically in white). Different cell types are designated by the layer location of their cell body and a descriptor of soma and dendrite geometry, given in different colours on the left side.
