Figure 4.
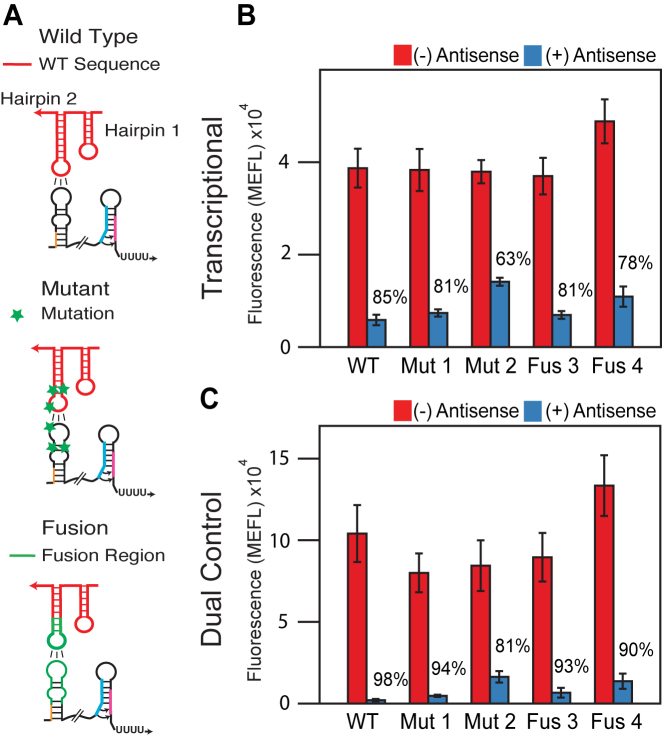
The dual transcription/translation control strategy functions across orthogonal pT181 mutants and chimeras. (A) Schematics of the interactions between the dual control sense target region and the corresponding cognate antisense RNA for wild type, specificity mutants and chimeric fusions engineered to change the specificity of the antisense–attenuator interactions. Sequences and structures are shown in Supplementary Figure S12. (B) Functional characterization of the transcriptional wild type pT181 repressor (WT), two mutants (Mut 1,2) (2) and two chimeric fusions (Fus 3,4) (29). Each repressor contained the wild type terminator region depicted in Figure 2A. Functional characterization and data presentation as in Figure 2. Error bars represent standard deviations of at least seven biological replicates. (C) As in (B) except with each repressor configured as a dual transcription/translation controller. Using the dual control strategy improves the repression of the transcriptional attenuators. Averages and standard deviations plotted in (B) and (C) are presented in Supplementary Table S5 to allow for comparison within orders of magnitude.