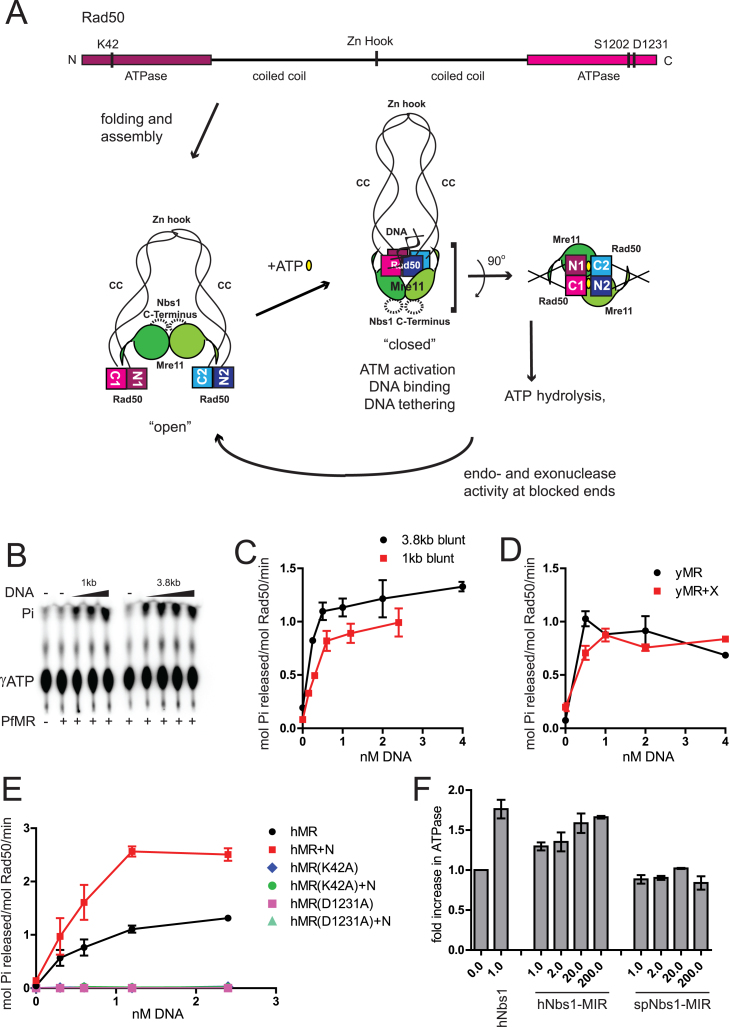
Figure 1.
DNA stimulates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis by MR/MRN(X) complexes. (A) A schematic of the MRN complex and ATP-induced changes in MRN conformation. A linear map of human Rad50 shows the positions of important conserved residues that were mutated in this study. Intramolecular folding of coiled coil brings the terminally placed ATPase domains together. Coiled coils (CC) from two Rad50 molecules interact through their Zn-hook motifs (Zn Hook). Mre11 nuclease/dimerization domain and the capping domain connected to the linker binds to the coiled coils of Rad50. The binding of ATP induces dimerization of ATPase domains and extensive conformational changes in the MRN complex. This ‘closed’ state exhibits higher affinity for DNA ends and promotes DNA tethering. A DNA helix is bound to the Rad50 ATPase domains as shown (20,22). ATP hydrolysis leading back to an ‘open’ state is required for Mre11 endonuclease activity and promotion of 5΄ to 3΄ resection. The Rad50 ATPase domains, Mre11 nuclease domains and Nbs1 Mre11-interacting-region constitute the catalytic core of the complex. In the absence of ATP, the catalytic head is in an ‘open’ conformation and the Mre11 nuclease sites are accessible. Rad50 ATPase domains dimerize in trans in the presence of ATP (yellow ovals), forming two functional sites as shown. ATP is engaged by Walker A motif K42 from one Rad50 and signature motif S1202 from the other Rad50. (B) PfMR (50 nM) was incubated with [γ- 32P]ATP in reactions containing 1–4 nM dsDNA (either 1 or 3.8 kb long, as indicated), 50 μM total ATP and 5 mM MgCl2 at 65°C for 1 h. Released Pi was separated by thin layer chromatography and analyzed by phosphorimager. (C) Quantitation of ATP hydrolysis assays as shown in (B). (D) yMR (50 nM) was assayed for ATP hydrolysis with equimolar Xrs2 as indicated in (B) but at 30°C for 1 h. Reactions contained 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 or 4.0 nM 1 kb dsDNA. (E) Human MR (50 nM) was assayed for ATP hydrolysis as in (B) with equimolar Nbs1 as indicated using 0.3, 0.6, 1.2 or 2.4 nM 1 kb dsDNA at 37°C for 1 h. hMR mutant complexes with K42A or D1231A mutations were assayed similar to wild-type (WT) hMR as indicated. Error bars indicate standard deviation from three replicates. (F) ATP hydrolysis by hMR (50 nM) was measured in the presence of 2.4 nM 1 kb linear DNA and either full-length or truncated versions of the hNbs1 (a.a. 637–686) or spNbs1 polypeptides (a.a. 474–531). The molar ratio of the Nbs1 protein compared to hMR is as indicated. Results are from three independent experiments and error bars indicate standard deviation.