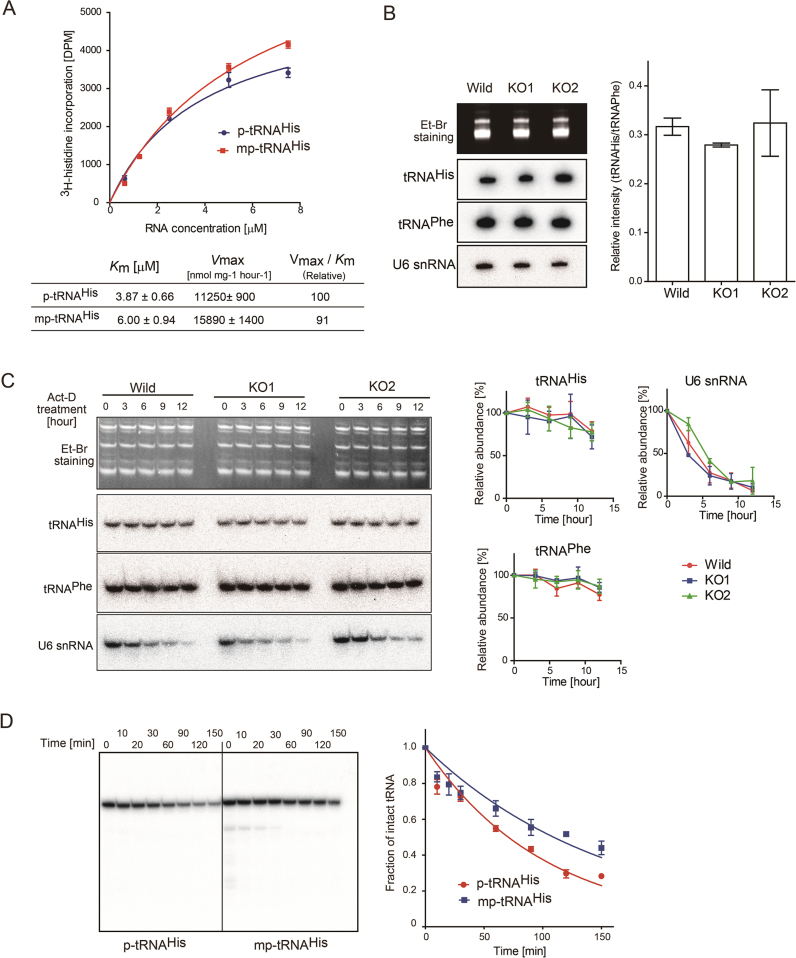
Figure 5.
Stability of tRNAHis with 5΄-monomethylmonophosphate. (A) Aminoacylation of p-tRNAHis and mp-tRNAHis by histidine tRNA synthetase in vitro. The steady-state kinetics parameters were calculated. (B) Steady-state levels of tRNAHis species in wild-type (HEK293T) and BCDIN3D knockout cells (KO1 and KO2). The amounts of tRNAHis in wild-type HEK293, KO1 and KO2 cells were analyzed by northern blotting. Quantification of the ratios of the band intensities of tRNAHis and tRNAPhe. (C) In vivo stabilities of tRNAHis. Wild-type HEK293T and KO cells were treated with actinomycin-D (Act-D) for 12 h. The stabilities of tRNAHis from the cells were analyzed by northern blotting, and quantified. The intensities of the bands of tRNAHis (or tRNAPhe or U6 snRNA) at zero time were designated as 1.0, and the relative amount of tRNAHis (or tRNAPhe or U6 snRNA) was quantified. (D) The in vitro decay of tRNAHis species with 5΄-monomethylmonophosphate (5΄pm-tRNAHis) and with 5΄-monophosphate (5΄p-tRNAHis) was performed using cytoplasmic extracts, and the amounts of intact tRNAHis species were quantified. The intensities of the bands of intact 32P-tRNAHis at zero time were designated as 1.0, and the relative amounts of tRNAHis were quantified. Bars in graphs in (A)–(D) are SD of more than three independent experiments.