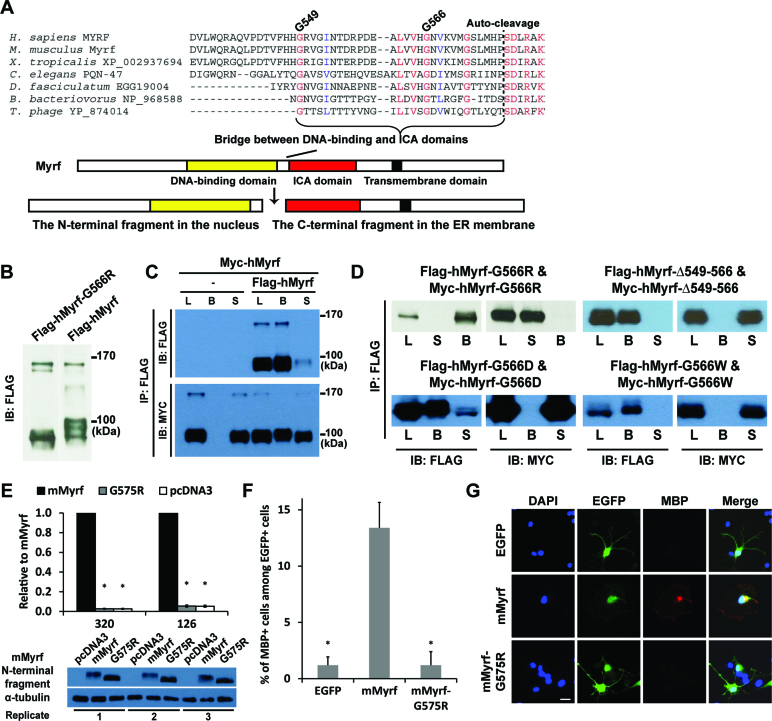
Figure 4.
Homo-trimerization is mediated by the bridge region between the DNA-binding and ICA domains and is essential for the functions of Myrf N-terminal fragments. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of the bridge region. (B) The G566R mutation did not interfere with the proteolytic processing of hMyrf. (C) An immunoprecipitation experiment showed that hMyrf N-terminal fragments self-associate, as reported before (14,15). (D) The self-association of hMyrf N-terminal fragments is not observed for the mutants. Same constructs with Flag and Myc tags were co-expressed in HEK293FT cells. Cell lysate (L) was subject to immunoprecipitation with Flag beads, leading to the bound (B) and sup (S) fractions. (E) The transcriptional activity of mMyrf-G575R is much weaker than that of mMyrf and is in fact as low as that of pcDNA3. The transcriptional activity of mMyrf was set to 1, and the reported values are means and standard errors of three biological replicates. *P < 0.001 by two-tailed one sample Student's t test with Bonferroni correction. (F and G) mMyrf-G575R failed to drive the in vitro differentiation of primary rat OPCs. EGFP, mMyrf or mMyrf-G575R was transfected into primary rat OPCs. After two days of culture in a proliferation condition that deters spontaneous differentiation, we determined the fraction of transfected cells (marked by EGFP) that had differentiated to express MBP. The reported values are means and standard errors of 5 biological replicates. *P < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student's t test with Bonferroni correction. Scale bar, 10 μm. IP: immunoprecipitation. IB: immunoblotting.