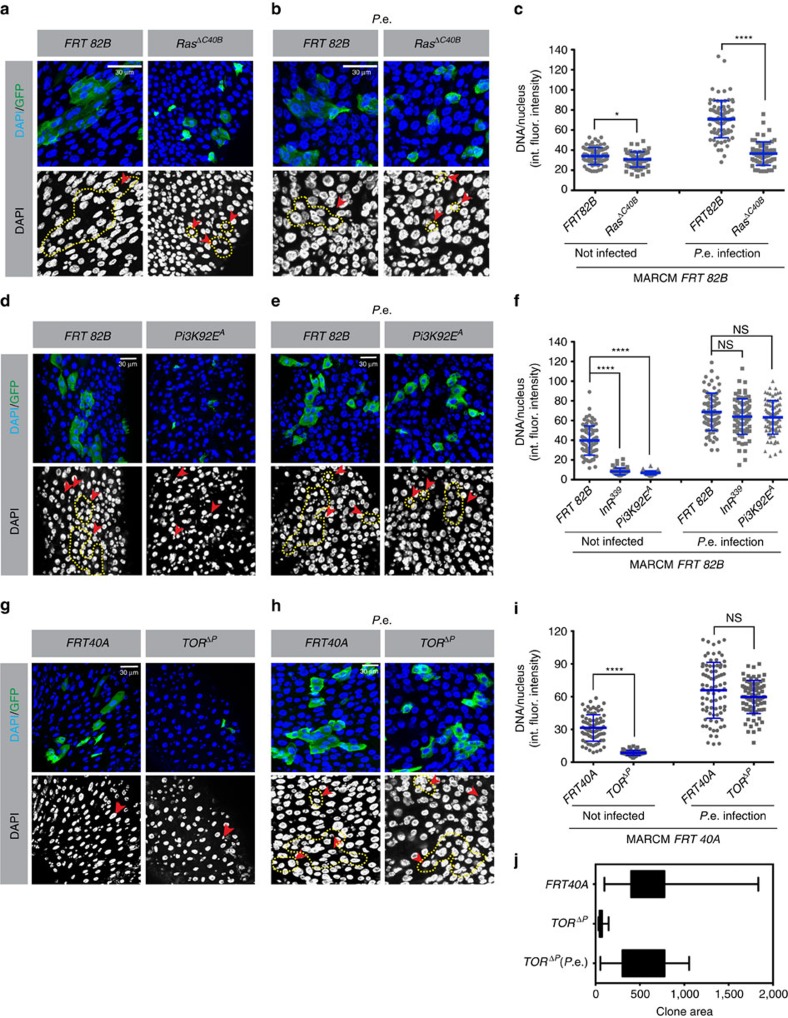
Figure 3. Clonal growth and EC ploidy affected by Ras Pi3K TOR and P.e. infection.
Ras85DΔC40B-, Pi3K92EA- or TORΔP-null mutant clones were made using the MARCM system. At 5 days after clone induction, midguts were dissected. Integrated DAPI intensity/nucleus was measured to determine ploidy. Clones were marked with GFP (green) and stained for DNA (blue). Clone boundaries are outlined by yellow dashed lines. (a) Flies raised on normal food. Left panel indicates FRT control and right panel Ras85D-mutant clones. (b) At 2 days after clone induction, flies were orally infected with P.e. for 24 h. Left panel indicates FRT control and right panel Ras85D-null mutant clones. (c) Quantification of DNA content/nucleus in clonally marked cells for (a,b). A total of 100 GFP+ nuclei from 10 midguts total were scored for each genotype. Ras85D-mutant cells had a slightly lower ploidy than wild-type control cells in normal conditions. Ras85D-mutant cells could not divide or become hyperpolyploid following stimulation by P.e. infection. int. fluor. intensity, integrated fluorescent intensity. (d–f) Experiments similar to those shown above, but using a null mutation in Pi3K or InR. A total of 80 GFP+ nuclei from 10 (control, InR mutant) or 20 (Pi3K mutant) midguts were scored. Pi3K- and InR-mutant cells had lower ploidy and reduced cell size under normal culture conditions, and appeared to be arrested in the diploid state. However, P.e. infection induced these mutant cells to divide and differentiate high ploidy ECs. Pictures of InR-mutant clones can be found in Supplementary Fig. 4 (d,e). (g–j) A similar experiment as above, but with TOR-mutant clones. (j) Quantification of clone areas (yellow dashed line). A total of 80 GFP+ nuclei from 10 (control) or 25 (TOR mutant) midguts were counted for each genotype. TOR-mutant cells arrested as diploids in normal culture (right panel (g)), but P.e. infection induced these mutant cells to proliferate and generate normally polyploid ECs (right panel (h)). Error bars represent s.d. Student's t-test was used to determine statistical significance (*P=0.0108, ****P<0.0001, NS P>0.05). All experiments were repeated three times.