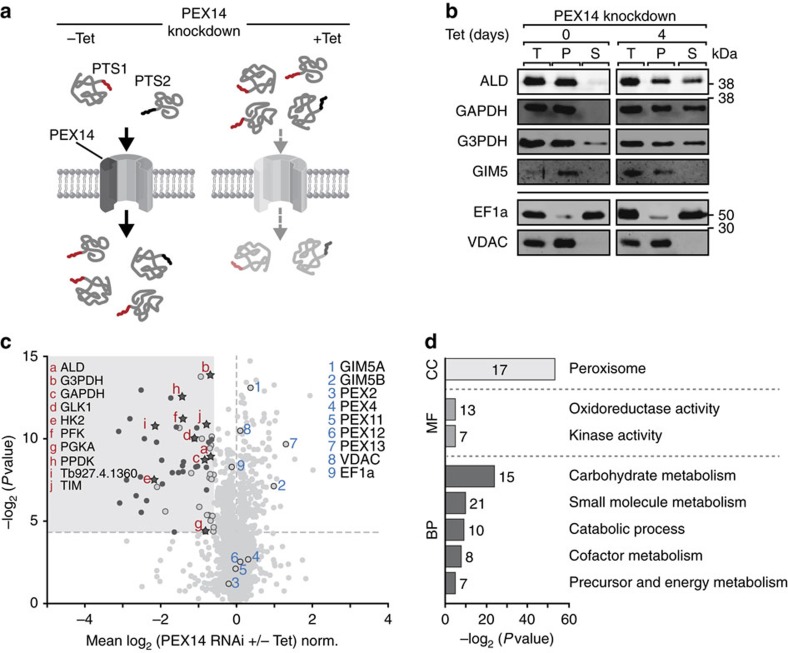
Figure 6. Targeting PEX14 to reveal proteins imported into glycosomes.
(a) PTS1- and PTS2-dependent import of nuclear-encoded glycosomal matrix proteins requires PEX14 (−Tet), a core component of the glycosomal protein import machinery. Inducible RNAi-mediated knockdown of PEX14 (+Tet) prevents protein import into glycosomes and leads to an accumulation of import substrates in the cytosol over time. PTS, peroxisomal targeting sequence. (b) Immunoblot analysis of whole cells (T), glycosome-containing pellet (P) and soluble (S) fractions of uninduced (−Tet, 0 days) and induced (+Tet, 4 days) PEX14-RNAi cells. Shown are the abundance levels of the glycosomal matrix proteins fructose bisphosphate aldolase (ALD), glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH) and the glycosomal integral membrane protein 5 (GIM5) in the different samples. EF1a and VDAC serve as cytosolic and mitochondrial marker protein, respectively. (c) Volcano plot of SILAC-PEX14-RNAi data. PEX14-RNAi cells were differentially labelled using SILAC including a label switch. Subsequently, the glycosome-containing fractions from induced (+Tet) and uninduced (−Tet) PEX14-RNAi cells were analysed by LC-MS (n=3). Proteins with a mean log2 ratio of less than or equal to −0.59 and P value<0.05 (n=3) were considered significantly decreased in abundance following PEX14 knockdown (shaded area). Stars, known glycosomal proteins involved in glycolysis annotated by protein name or gene ID; dark grey dots, further glycosomal proteins affected by PEX14 knockdown; light grey dots, other proteins. Glycosomal membrane proteins including GIM5A, GIM5B and several peroxins (PEX proteins) as well as the mitochondrial membrane and the cytosolic marker protein VDAC and EF1a, respectively, are highlighted. norm., normalized. (d) GO term enrichment analysis of proteins with a significantly decreased abundance in glycosome-containing pellet fractions following PEX14 knockdown. P values after Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR <0.05) correction were plotted against their corresponding GO terms from the three main domains ‘cellular component' (CC), ‘molecular function' (MF) and ‘biological process' (BP). The number of proteins assigned to a given term is indicated.