Figure 6. Schematic model of epithelial and stromal signaling pathways affected in GOF β-catenin mice during implantation and decidualization.
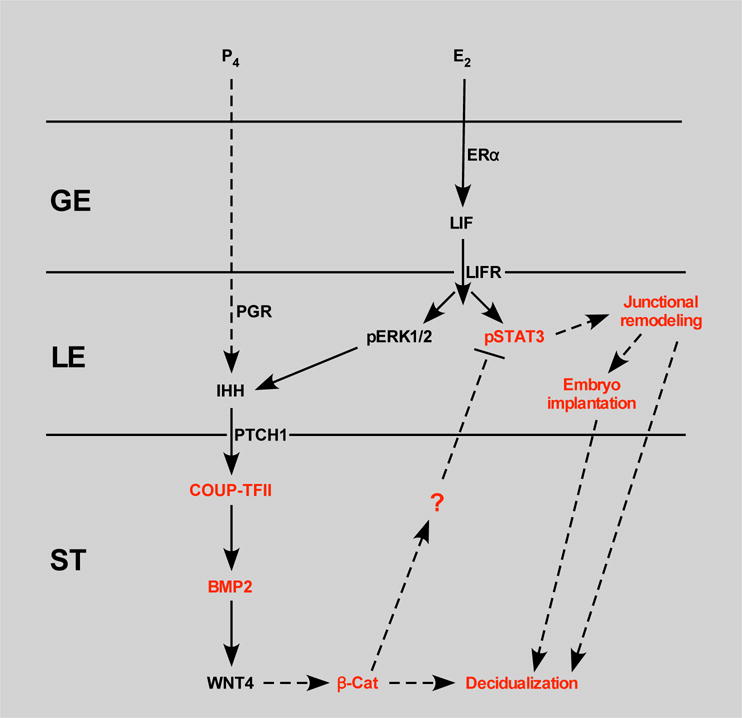
Estradiol signals through its receptor, ERα, in the glandular epithelium (GE) to induce LIF expression. LIF signals through its receptor, LIFR, in the luminal epithelium (LE) to activate ERK and JAK/STAT signaling. ERK signaling in concert with progesterone signaling through PR induces expression of IHH in the LE. IHH signals through PTCH1 in the stroma (ST) to up regulate the COUP-TFII-BMP2-WNT4 pathway. WNT4 may then signal through β-catenin to regulate decidualization. GOF β-catenin perturbs this pathway presumably by regulating expression of an unknown factor that signals to the LE to affect phosphorylation of STAT3 leading to altered expression of junctional remodeling factors and impaired embryo implantation and decidualization. Black lettering, un-altered expression; red lettering, altered expression/function.
