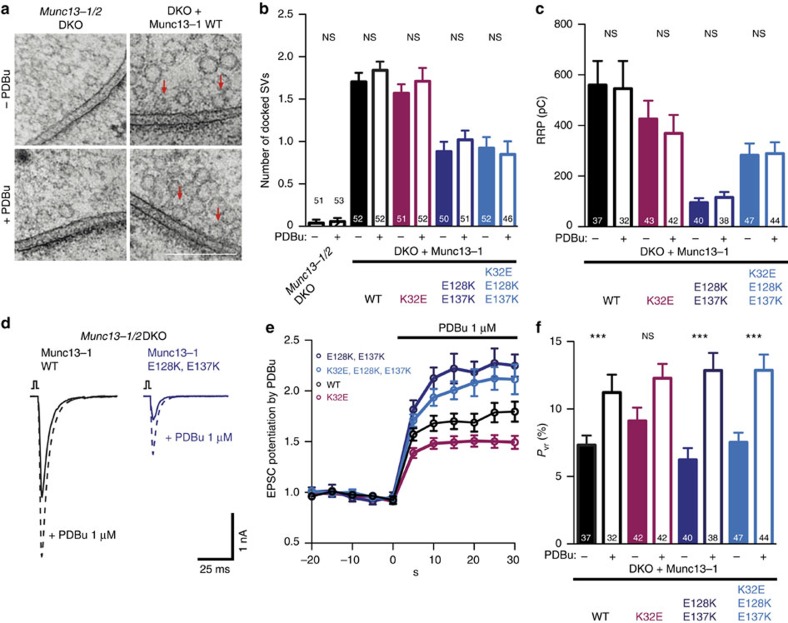
Figure 6. Activation of the C1 domain by DAG/phorbol ester is downstream of the regulation of C2A domain.
(a) Representative electron micrographs of synapses showing docked synaptic vesicles (indicated by red arrows) from Munc13-1/2 DKO synapses and DKO rescued with Munc13-1 WT. Scale bar, 200 nm. (b) Plot of docked synaptic vesicles from the Munc13-1/2 DKO and DKO synapses rescued with Munc13-1 WT and Munc13-1 C2A homodimerization- and heterodimerization-disrupting mutants with or without PDBu. (c) Plot of RRP charge of DKO neurons rescued with Munc13-1 WT and Munc13-1 C2A homodimerization- and heterodimerization-disrupting mutants with or without PDBu. (d) Example traces of evoked EPSC amplitudes from Munc13-1/2 DKO rescued with Munc13-1 WT in black and Munc13-1 that favours the homodimerization state E128K, E137K in blue (solid lines) and their corresponding EPSCs after PDBu application (dotted lines). (e) Potentiation of AP-evoked EPSC amplitudes induced by 1 μM of PDBu. PDBu amplitudes were calculated by normalizing the EPSC amplitude in PDBu with the preceding EPSCs recorded in control extracellular solution. (f) Vesicular release probability Pvr for Munc13-1 WT and mutant rescues with or without PDBu. Numbers in bar graphs are n values for each group. Data are expressed as mean±s.e.m. For each mutant group, significance and P values were calculated by comparison with the non-PDBu-treated group using the unpaired Student's t-test: Mann–Whitney. ***P<0.001.