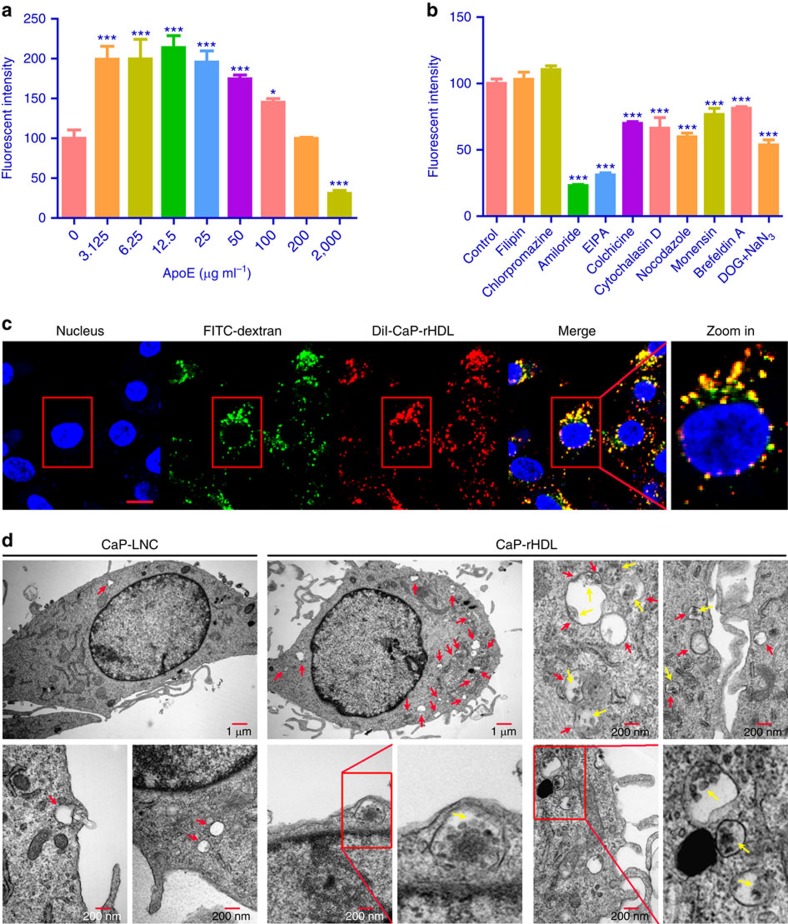
Figure 3. Cellular uptake of CaP-rHDL in C6 glioblastoma cells via the macropinocytosis pathway.
(a) Cellular association of DiI-CaP-rHDL in the presence of ApoE3 at the concentrations ranged from 0 μg ml−1 to 2 mg ml−1 in C6 glioblastoma cells. (b) Cellular association of DiI-CaP-rHDL in the presence of different endocytosis inhibitors. For a and b, data represent mean±s.d. (n=3). *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 significantly different with that of the non-treated control. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis. (c) Colocalization of DiI-CaP-rHDL to macropinocytosis marker FITC-70kDa dextran. Scale bar, 10 μm. (d) Macropinocytosis-mediated internalization of CaP-rHDL observed under TEM. C6 glioblastoma cells were incubated with CaP-LNC or CaP-rHDL for 3 h, fixed and processed for observation under thin-section electron microscopy. Red arrows indicated macropinosomes. Yellow arrows indicated CaP-rHDL internalized via macropinocytosis.