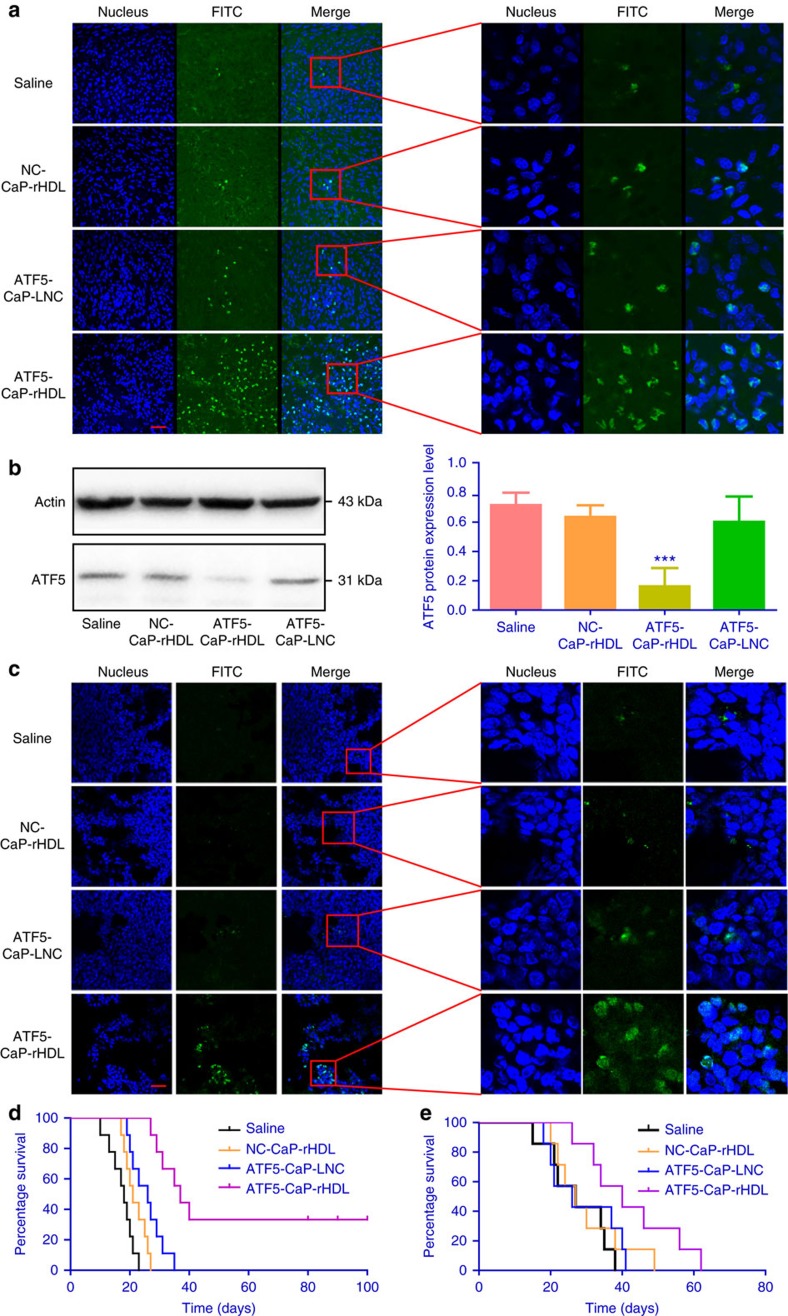
Figure 9. ATF5-CaP-rHDL induced apoptosis at the glioblastoma site and prolonged the survival of mice bearing intracranial glioblastoma.
(a) Nude mice bearing intracranial C6 glioblastoma treated with saline, NC-CaP-rHDL, ATF5-CaP-LNC or ATF5-CaP-rHDL every 2 days for four times at the siRNA dose of 0.36 mg kg−1 (n=3). One day after the last injection, the animals were killed with the brains collected, sectioned and stained using a TUNEL kit. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) NOD/SCID mice bearing intracranial GICs glioblastoma treated with saline, NC-CaP-rHDL, ATF5-CaP-LNC or ATF5-CaP-rHDL every 3 days for five times at the siRNA dose of 0.36 mg kg−1 (n=3). One day after the last injection, the animals were killed with the brains collected. ATF5 level at the tumor regions was quantified via western blot. The significance of the differences was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test. ***P<0.001, significantly different with that of the saline group. (c) NOD/SCID mice bearing intracranial GICs glioblastoma were treated with saline, NC-CaP-rHDL, ATF5-CaP-LNC or ATF5-CaP-rHDL every 3 days for five times at the siRNA dose of 0.36 mg kg−1 (n=3). One day after the last injection, the animals were killed with the brains collected, sectioned and stained using a TUNEL kit. Scale bar, 50 μm. (d) Kaplan–Meier survival curve of mice bearing intracranial C6 glioblastoma treated with saline, NC-CaP-rHDL, ATF5-CaP-LNC or ATF5-CaP-rHDL every 2 days for four times at siRNA dose of 0.36 mg kg−1 (n=9). (e) Kaplan–Meier survival curve of mice bearing patient-derived GICs glioblastoma treated with saline, NC-CaP-rHDL, ATF5-CaP-LNC or ATF5-CaP-rHDL every 3 days for five times at siRNA dose of 0.36 mg kg−1 (n=7).