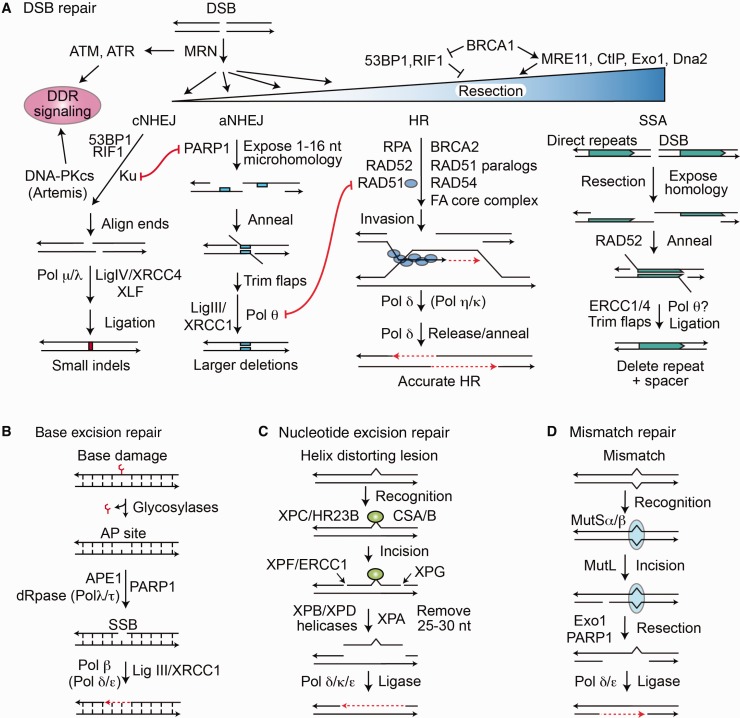
Figure 1.
DNA repair pathways in mammalian cells. A) Double-strand breaks (DSBs) activate DNA damage response signaling including checkpoint arrest through ATM, ATR, and DNA-PKcs. DSB repair pathway choice is determined by the amount of 5’ end resection at the DSB, inhibited by 53BP1/RIF1, promoted by BRCA1/CtIP. MRE11 initiates limited end resection, and this is followed by Exo1/EEPD1 and Dna2 nucleases for extensive resection. 53BP1/RIF1 and Ku protect DSB ends from resection, promoting classical nonhomologous end joining (cNHEJ). PARP1 competes with Ku and promotes limited end resection for alternative nonhomologous end joining (aNHEJ). RAD51 catalyzes invasion by the resected 3' end into the sister or other homologous sequences, and Pol δ catalyzes repair synthesis across the DSB. The amount of 3’ end resection regulates DSB pathway choice. cNHEJ requires little or no end resection, aNHEJ requires limited resection, and homologous recombination (HR) and single-strand annealing (SSA) require extensive resection. DNA polymerase θ (Pol θ) promotes a microhomology search by the opposing 3’ single strands after short resection in aNHEJ. The HR subpathway SSA requires extensive end resection to expose large homologous regions, usually direct repeats, with RAD52 promoting annealing, producing large deletions between direct repeats. B) Base excision repair repairs minor lesions (eg, oxidized bases), promoted by PARP1. Repair intermediates include an abasic site and nicking of the DNA backbone, with short gap filling by Pol β. C) Nucleotide excision repair (NER) repairs large helix-distorting lesions and involves excision of about 15 nucleotides on either side of the lesion, followed by gap filling. GG-NER and TC-NER differ in lesion recognition by XPA or CSA/B, respectively. D) Mismatch repair involves recognition of the mismatched nucleotide by MutSα/β, followed by strand nicking with MutL, extensive resection with Exo1, and repair synthesis. DNA ligases catalyze religation, the final step in all pathways. aNHEJ = alternative nonhomologous end joining; cNHEJ = classical nonhomologous end joining; DDR = DNA damage response; DSB = double-strand break; HR = homologous recombination; SSA = single-strand annealing.