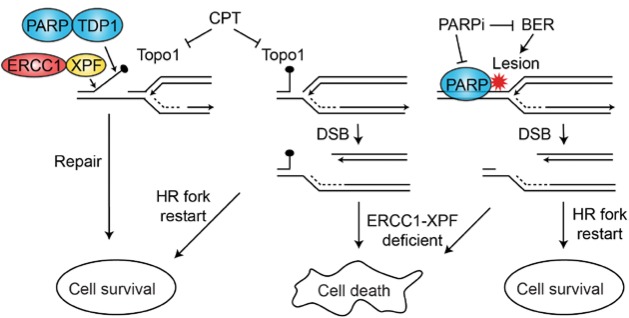
Figure 5.
Synthetic lethal targeting with PARP1 and ERCC1-XPF deficiencies. Camptothecin traps TopoI covalently onto DNA, blocking replication. Repair can proceed via a PARP-TDP and ERCC1-XPF1 pathway (left) or by fork repair and restart via homologous recombination; PARP1 inhibition, coupled with ERCC1-XPF deficiency, is synthetically lethal (middle). PARP1 inhibition also blocks base excision repair of single-strand lesions that block replication; these lesions are similarly lethal with ERCC1-XPF deficiency (right). BER = base excision repair; CPT = camptothecin; DSB = double-strand break; HR = homologous recombination.