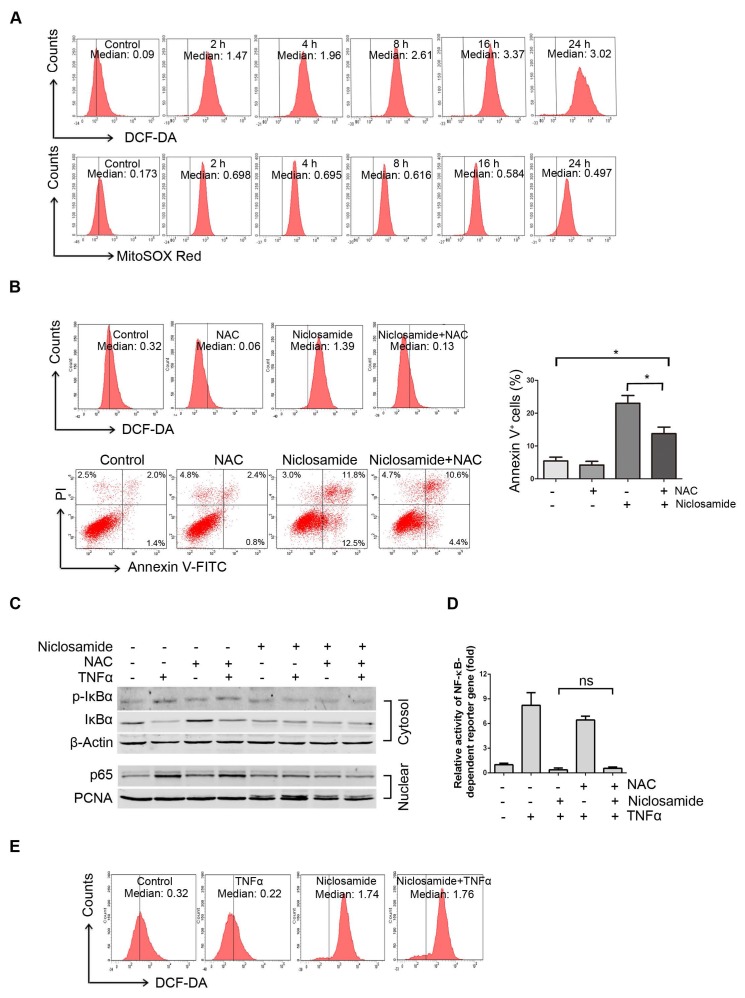
Figure 4.
Niclosamide increases intracellular and mitochondria specific ROS in uveal melanoma cells. (A) Mel270 cells were treated with niclosamide (4 μmol/L) for indicated times, and then stained with CM-H2DCF-DA (for measurement of intracellular ROS) or MitoSOX Red Reagent (for measurement of mitochondria specific ROS) for 1 h. ROS was determined by flow cytometer. The median intensity of DCF-DA (top) or MitoSOX Red (bottom) is shown. (B) Mel270 cells were pre-incubated with NAC (20 mmol/L) for 1 h, and then exposed to niclosamide (4 μmol/L) for 24 h. ROS and apoptosis were evaluated by flow cytometry (left). Mean ± SD of apoptotic cells from 3 independent experiments are shown (right). *, p< 0.05,one-way ANOVA, post hoc comparisons, Tukey's test. (C) Mel270 cells were exposed to niclosamide (4 μmol/L) for 24 h with or without NAC (20 mmol/L), and then stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/mL) for 30 min. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were analyzed by Western blot for p-IκBα, IκBα (cytosol) and p65 (nuclear). (D) Mel270 cells were transiently co-transfected with NF-κB-TATA-Luc reporter constructs (0.5 μg) and Renilla luciferase reporter constructs (10 ng). Twenty-four hours later, the cells were exposed to different concentrations of niclosamide in the absence or presence of NAC for 16 h, followed by stimulation with TNFα (20 ng/mL) for 8 h. Luciferase activity was detected at the end of treatment. Results are fold change ± SD. n.s., no significant difference, one-way ANOVA, post hoc comparisons, Tukey's test. (E) Mel270 cells were treated with niclosamide and TNFα, and then ROS was detected by flow cytometry.