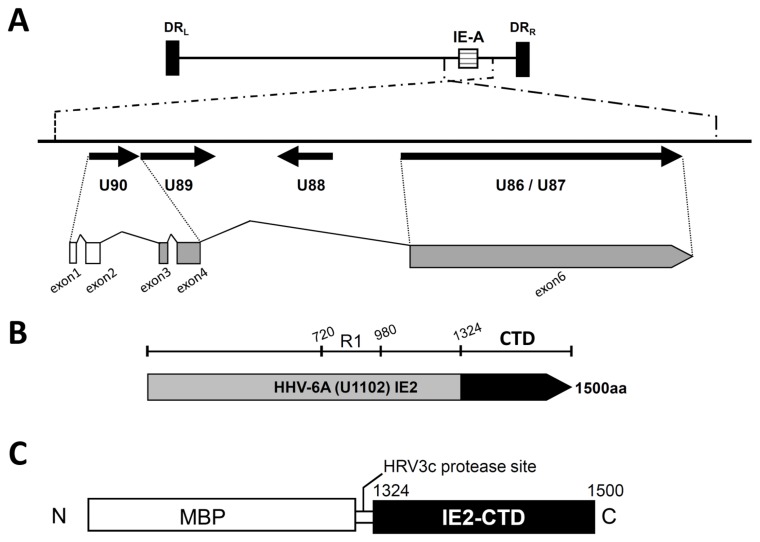
Figure 1.
HHV-6A U1102 IE2 and the C-terminal structural domain IE2-CTD. (A) A schematic diagram of the immediate early A locus of HHV-6A strain U1102. The upper panel shows the entire HHV-6A strain U1102 genome including direct repeat regions left (DRL) and right (DRR) and the major immediate early A locus (IE-A). The lower panel is an enlarged view of the ORFs at the IE-A locus (represented by arrows). Exons 1 and 2 (white) are non-coding, and exons 3, 4 and 6 (grey) generate the IE2 protein. Exons 3 and 4 are derived from U90, and exon 6 is from U86/87. (B) The full length HHV-6A IE2. The black region is the C-terminal domain of IE2 (IE2-CTD), the focus of this study. R1 (720–980) indicates the serine/arginine repeat region. (C) The HHV-6A IE2-CTD construct used for expression in Escherichia coli. The 1324–1500 region of HHV-6A (IE2-CTD) is fused to maltose binding protein (MBP) with a human rhinovirus (HRV) 3c protease site at the domain boundary.