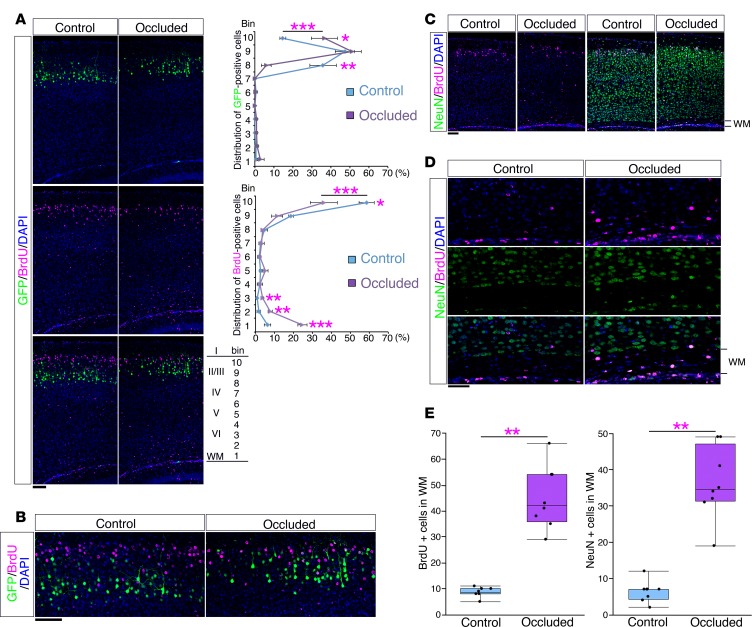
Figure 6. The mouse model showed an altered neuronal alignment.
(A) After transfection of GFP plasmid at E15.0, a sham operation (Control) or maternal uterine artery occlusion (Occluded) was performed at E16.5 and followed by BrdU injection at E17.0. Brains were analyzed at P10. Sections were immunostained with anti-BrdU antibody (magenta). Right panels show the bin analysis of the distribution of GFP-positive cells and BrdU-positive cells (mean ± SEM; n = 4, respectively). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) High-magnification images of the superficial areas of the neocortices in A. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) A sham operation or maternal uterine artery occlusion was performed at E16.5 and followed by BrdU injection at E17.0. Brains were analyzed at P10. Sections were immunostained with anti-NeuN antibody (green) and anti-BrdU antibody (magenta). Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) High-magnification images of the white matter (WM) in C. Scale bar: 50 μm. (E) The number of BrdU-positive cells (left) and NeuN-positive cells (right) in the WM (n = 8, respectively) are shown. ***P < 0.001, Welch’s t test. Each point represents an individual mouse. Box-and-whisker plots were used to graphically represent the median (line within box), upper and lower quartiles (bounds of box), and maximum and minimum values (top and bottom bars).