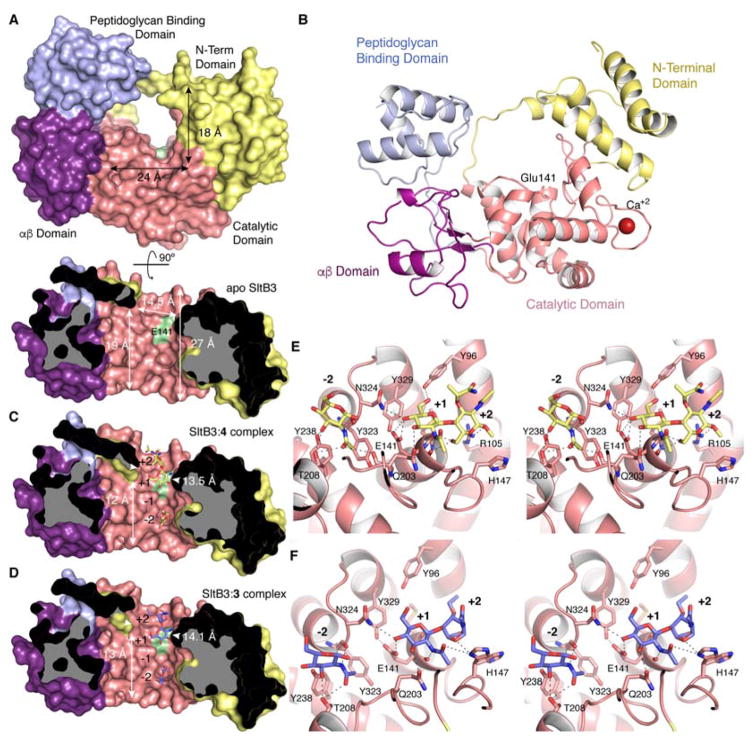
Figure 3.
(A) The three-dimensional structure of apo SltB3 for the frontal view (top) and the cross-section view from 12 o’clock downward (bottom) drawn as Connolly surface. The N-terminal domain is in yellow, the catalytic domain is in pink, the αβ-domain is in magenta and the peptidoglycan-binding domain is in light blue. The surface position of the proposed catalytic Glu141 is indicated in green. (B) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of apo SltB3. Each domain is colored as in panel A. (C) Same view of the active site for the SltB3:4 complex. Compound 4 is depicted as yellow sticks for carbons. (D) Active site of the SltB3:3 complex with compound 3 depicted as blue sticks for carbons. Panels B and C show how the peptidoglycan and its products of turnover would span the opening of the annulus, the site of catalysis. The protein dimensions within the cavity for the two complexes are different (indicated) compared to the apo structure. (E) Stereo view showing the interactions stabilizing compound 4 in the active site of SltB3. Substrate is depicted as capped sticks and colored in yellow for C atoms, red for O atoms and dark blue for N atoms. (F) Stereo view showing the interactions stabilizing compound 3 in the active site of SltB3. Ligand 3 is depicted as capped sticks and colored in light blue for C atoms, red for O atoms and dark blue for N atoms. The two conformational states for His147 are shown. Protein residues (in panels E and F) involved in stabilization are depicted as capped sticks and labeled. Interactions are represented with dashed lines.