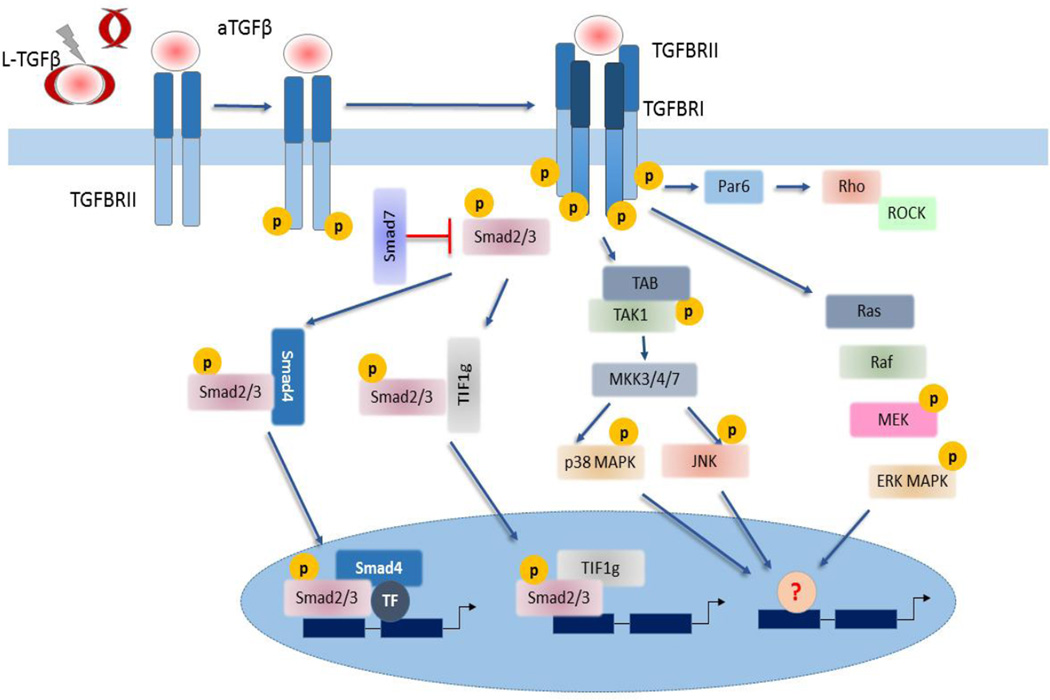
Figure 1. TGFβ signaling pathway.
TGFβ factors are secreted as complex inactive protein bound to latency-associated peptide, and the latent TGF- TGFβ1 binding protein-1, called latent TGFβ (L-TGFβ). After dissociation from the complex, TGFβ binds to membrane-bound type I and II receptors. Upon binding, the constitutively activated type II receptor (TGFΒRII) recruits and activates by phosphorylation the type I receptor (TGFΒRI), which then activates canonical (smad) or non-canonical (TAK1-p38 MAPK-JNK) signaling pathways. After activation by phosphorylation, Smad2/3 form a trimer with smad4 and accumulate in nucleus where the complex binds to master transcription factors for regulation of gene transcription. Another transcription factor TIF1γ can compete with Smad4 and bind to Smad2/3. Alternatively, TGFβ can signal via JNK and p38MAPK signaling, ERKMAPK and small Rho GTPases.