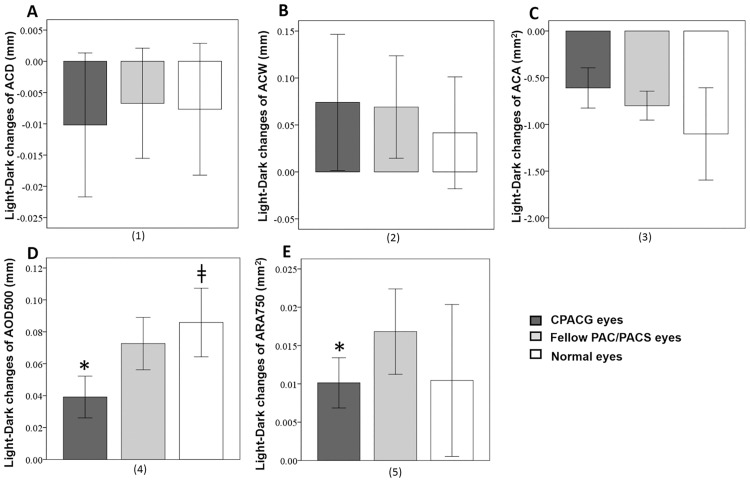
Fig 3. Light-to-dark changes of anterior chamber parameters in CPACG eyes, fellow PAC/PACS eyes, and normal eyes.
A: There was no difference in light-to-dark changes of ACDs among the three groups. B: There was no difference in light-to-dark changes of ACWs among the three groups. C: There was no difference in light-to-dark changes of ACAs among the three groups. D: The light-to-dark changes of AOD500μm in CPACG eyes were smaller than those in their fellow PACS/PAC eyes and normal eyes. There was no difference in the light-to-dark changes of AOD500μm between PACS/PAC eyes and normal eyes. E: The light-to-dark changes of ARA750μm in CPACG eyes were smaller than those in their fellow PACS/PAC eyes. There was no difference in the light-to-dark changes of ARA750μm between PACS/PAC eyes and normal eyes. CPACG: chronic primary angle closure glaucoma; PAC: primary angle closure; PACS: primary angle closure suspect; ACA: anterior chamber area; AOD500μm: angle opening distance 500 μm from the scleral spur; ARA750μm: angle recess area 750 μm from the scleral spur; ACD: anterior chamber depth; ACW: anterior chamber width; *: significant difference between PACG eyes and fellow eyes (P<0.017); ‡: significant difference between PACG eyes and normal eyes (P<0.017); Error bars: 95% confidence interval (95% CI).