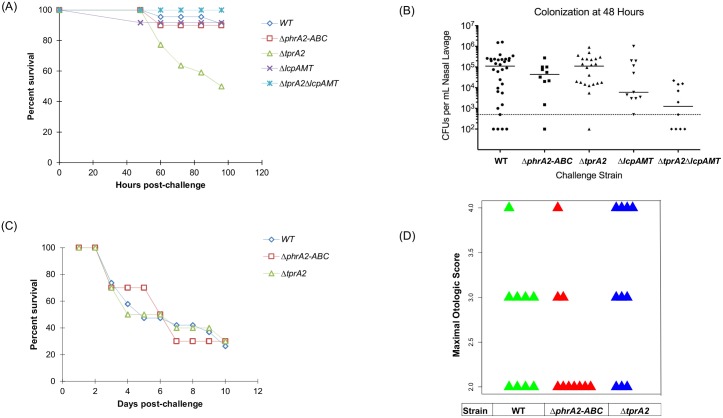
Fig 8. In vivo effects of TprA2/PhrA2 system.
(A,B) Analysis of PMEN1 strain SV36 WT and isogenic mutants ΔtprA2; ΔphrA2-ABC; ΔlcpAMT; and ΔtprA2ΔlcpAMT in the murine model with intranasal inoculations. (A) Percentage survival of mice after intranasal inoculation. Cohorts of at least ten mice were assessed for the duration of four days. Statistical significance relative to WT was calculated using Mann-Whitney U test; ‘*’, P-value<0.05. (B) Bacterial counts from nasal lavages of mice 48h post-inoculation. (C,D) Analysis of PMEN1 strain (4595-T23) WT and isogenic mutants ΔtprA2 and ΔphrA2-ABC in the chinchilla model of otitis media. (C) Percentage survival of chinchillas after transbullar inoculation. Cohorts of at least ten chinchillas were assessed for the duration of ten days. (D) Scatter plots illustrate the maximal otologic score for animals infected with WT (green), ΔphrA2-ABC (red) or ΔtprA2 (blue). Each triangle represents one animal. Otologic disease ranged from no disease to a ruptured tympanic membrane, where a score of ‘1’ is given for animals with mild or no disease, ‘2’ with moderate disease, ‘3’ with frank purulence, and “4” with tympanic membrane rupture.