Figure 5.
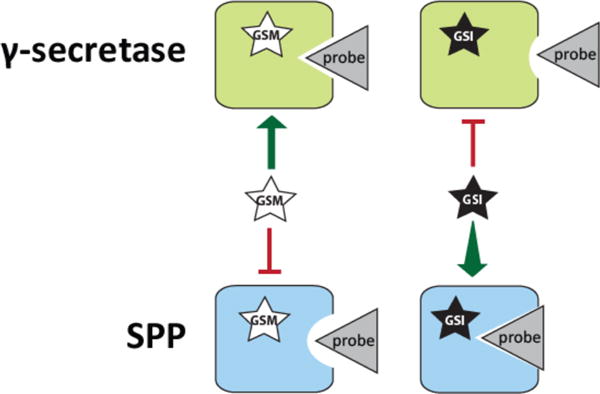
Model for the change in active site conformation of γ-secretase and SPP that occurs upon binding by GSIs and GSMs. We propose that the GSIs and GSMs studied here allosterically bind to γ-secretase and SPP, causing a conformational change in the active sites of the enzymes. Surprisingly, the induced conformational change is opposite for the two enzymes, as evidenced by their binding to active site-directed probes. Specifically, GSIs cause decreased binding between γ-secretase and probe while increasing binding between SPP and probe. GSMs cause little change in binding between γ-secretase and probe but reduce binding between SPP and probe. This suggests a model in which GSIs cause the active site of γ-secretase to assume a “closed” conformation but have the reverse impact on the active site structure of SPP.
