Figure 4.
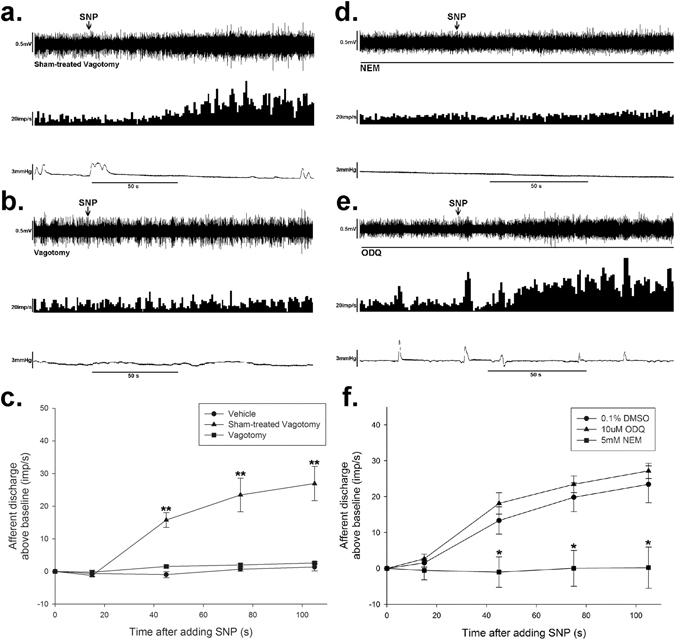
The excitatory effect of SNP was abolished by prior subdiaphragmatic vagotomy and S-nitrosylation blocker NEM. (a) Response of whole nerve activity before and after SNP administration on sham-operation rats. The upper trace shows the raw recording of whole nerve discharge, the middle trace is the number of nerve discharge in 3 s, and the lower trace shows corresponding intraluminal pressure. The arrows indicate the administration of SNP (0.16 mM). Sham-operation of vagotomy didn’t change the effect of SNP to increase the spontaneous afferent discharge. (b) Response of whole nerve activity to SNP on subdiaphragmatic vagotomy rats. SNP failed to increase the spontaneous afferent discharge. (c) Summary values showing that the excitatory effect of SNP (0.16 mM) was eliminated by vagotomy. n = 6 in each group, **P < 0.01 vs vehicle, Dunn’s post hoc test after a one-way ANOVA. (d) Response of whole nerve activity to SNP in the presence of NEM (5 mM). SNP (0.16 mM) failed to increase the spontaneous afferent discharge. (e) Response of whole nerve activity to SNP in the existence of ODQ (10 µM). ODQ didn’t change the excitatory effect of SNP on the spontaneous afferent discharge. (f) Summary values showing that the excitatory effect of SNP (0.16 mM) was eliminated by NEM (5 mM), while ODQ (10 µM) had no effect compared to the DMSO group. n = 6 in each group, *P < 0.05 vs DMSO group, Dunn’s post hoc test after a one-way ANOVA.
