Figure 1.
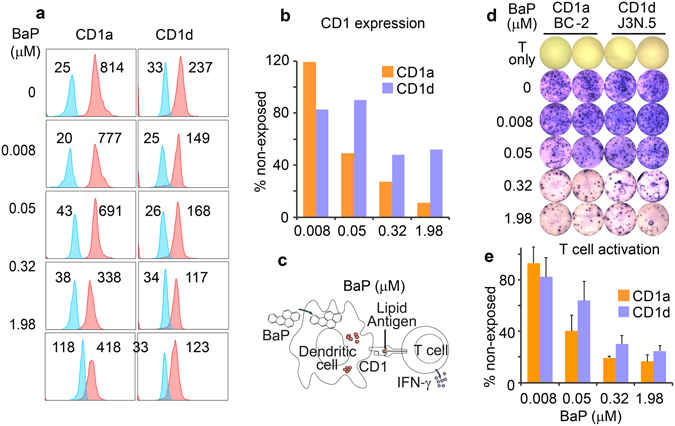
Inhibition of CD1 expression and T cell activation by BaP. CD1a and CD1d proteins (Red) on human DCs were tested by flow cytometry and plotted with non-stained controls that reflect the autofluorescence of BaP (Blue). To estimate CD1 expression, mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was labeled by the histogram (a). Then, the MFI of stained samples was normalized to that of non-stained samples and compared with non-exposed DCs (b). T cell activation represented by IFN-γ production was stimulated by DCs and tested with an immunospot assay, as schematically shown (c). The immunospot plate (d) and quantified results (e) show that the activation of CD1a-restricted BC-2 cells and CD1d-restricted J3N.5 cells was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by DCs exposed to BaP. Standard errors from technical replicates of each sample are shown. Data are from one experiment performed with blood cells obtained from an independent donor. Three experiments were performed with similar results.
