Figure 3.
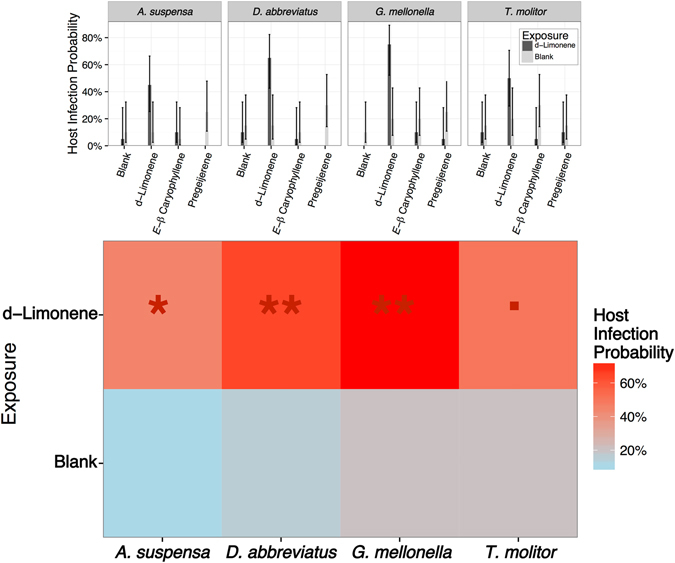
Parasitoid Learning Affects Alternate Host Infection. Prior exposure to d-limonene increases host infection probability for the natural host, D. abbreviatus, the host in which it is reared, G. mellonella, and the caribbean fruit fly A. suspensa. Cohorts of entomopathogenic nematode H. indica infective juveniles were exposed to blank controls or d-limonene then assayed in four-arm, sand-filled olfactometers where they responded to larvae paired with three common plant volatiles. Bars and error bars denote host infection probability and ninety-five percent confidence intervals respectively. Double asterisks denotes significant enhancement of infection probability at P < 0.01. A single asterisk denotes significant enhancement of infection probability at P < 0.05. A period denotes marginally significant enhancement of infection probability at P < 0.1.
