Figure 6.
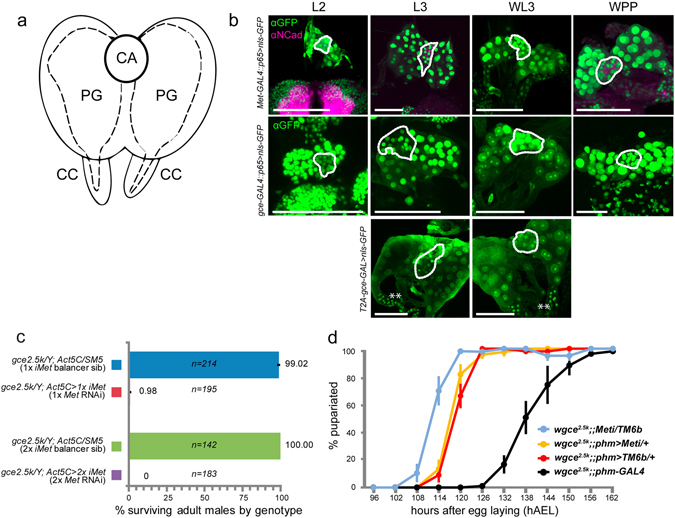
Presence of the JHRs in the ring gland. (a) Diagram of the endocrine tissues that comprise the larval ring gland, which includes the medial corpus allatum (CA), the paired lateral prothoracic glands (PG) that synthesize ecdysone, and the paired, basal corpora cardiaca (CC); (b) Confocal scans of the larval ring gland dissected from larvae expressing nls::GFP from either Met-GAL4::p65, gce-GAL4::p65, or gce-T2A-GAL drivers. Scans were taken from staged larvae from ~48 h after egg laying (AEL) (early L2 stage) to pupariation (WPP, ~120 h AEL). Where shown, N-cadherin labels the larval brain lobes and the CA. The position of the CA in each panel is indicated with a dotted line. (c) Global Met suppression was achieved by crossing Act5C-GAL4 into gce mutants to drive Met RNAi (45854 or 45852). RNAi function was verified via phenocopying the effects of global Met and gce deletion, which results in pupal mortality. (d) Delay in time to pupariation in gce 2.5k; phm > Met RNAi larvae (n = 177) vs. control lines (wgce;;Met-RNAi/Tm6b parental stock, n = 170, wgce 2.5k;;phm > TM6b line, n = 162, and wgce 2.5k; phm-GAL4 line, n = 335). Error bars: SEM. Scale bars, 50 µM. GFP (green or white), N-cadherin (magenta).
