Figure 6.
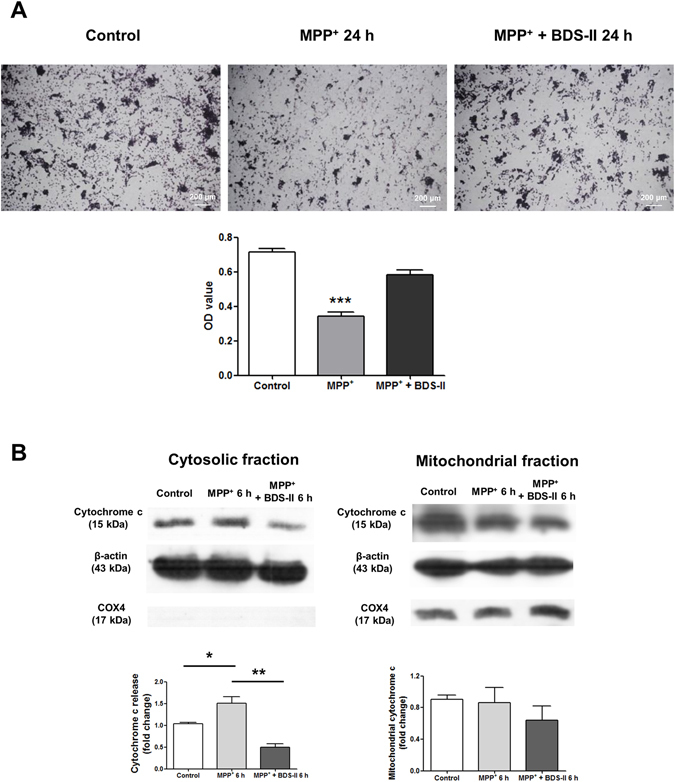
The neuroprotective effect of BDS-II against MPP+-induced SH-SY5Y cell death (A) Hemacolor-stained SH-SY5Y cells and MTT assays demonstrate that 100 nM BDS-II protected SH-SY5Y cells against 500 µM MPP+-induced neural cell death. The MTT assay demonstrated that only 48.23 ± 2.91% of cells survived after 24 h of 500 µM MPP+ treatment, whereas BDS-II enabled 81.68 ± 3.94% of cells to survive after 500 µM MPP+ treatment. (B) BDS-II blocked MPP+-induced cytochrome c release from the mitochondrial intermembrane space to the cytosol, which is a key step in the apoptosis signalling pathway. Experiments were repeated in triplicate, and data represent the mean ± standard error. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus the control value.
